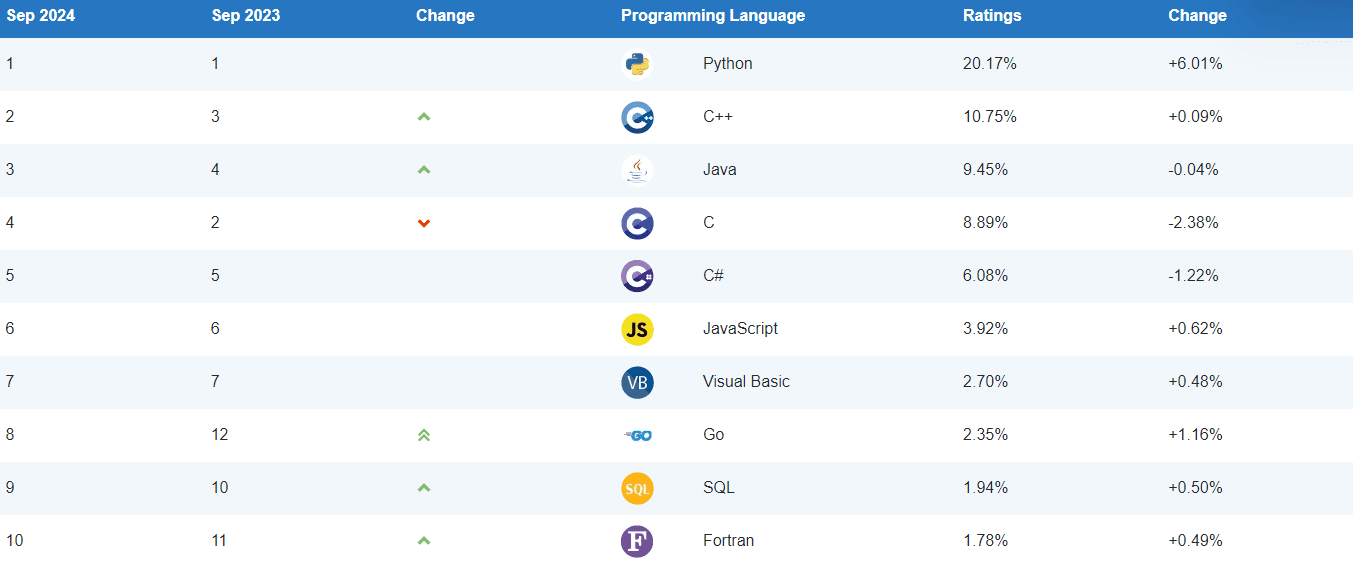
business resources
When Should I Start Learning Java and What is it For?
26 Sept 2024, 5:03 pm GMT+1
Java is one of the most popular programming languages in the world. As an open-source, object-oriented language, Java offers platform portability, security, performance and a massive open-source ecosystem.
Whether you're a student, entrepreneur or business professional, there are many good reasons to learn Java. This article provides guidance on when you should start and the key applications of Java today.
Why Learn Java?
Here are some of the main reasons Java is a great skill to learn:
Powering 3 Billion Devices
Java powers more than 3 billion devices worldwide. Its portable bytecode means that code written using Java developer outsourcing can run on any device with the Java Virtual Machine (JVM) installed. This portability spans mobile, desktop, web servers, embedded systems and more.
In-Demand Programming Language
Java consistently ranks as one of the most in-demand programming languages sought after by employers. Learning Java enhances careers for developers, software architects, QA engineers, data scientists, and other technical professionals across many industries.
Backbone of Enterprise Systems
Nearly 90% of Fortune 500 companies use Java to build and maintain enterprise applications and systems. Its robustness, security and scalability make it well-suited for large, complex business systems that require smooth integration across multiple platforms.
Leading the Big Data Revolution
Many prominent big data frameworks used to process and analyze large datasets are Java-based, including Apache Hadoop, Apache Spark and Apache Kafka. Java skills allow developers and data scientists to harness the power of big data.
Powering Android Apps
Java is the official language of Android app development. The Android SDK and APIs are Java-based, so learning Java is imperative for any mobile developer getting into Android.
These are just some of the many crucial real-world applications for Java today. Mastering it unlocks opportunities across industries.
When Should You Start Learning?
Java can be learned at different stages for different purposes:
High School Students
Java is commonly taught as a first language in high schools due to its clean syntax, OOP model and real-world applicability. Learning Java early fosters sharp analytical and problem-solving skills for future CS studies.
Undergraduate Students
Most university CS/CE curriculums require students to take at least one core Java module. Java builds a solid programming foundation applicable to specialized subjects like machine learning, app development, etc.
Career Changers
Many professionals make a career change into the tech industry via coding boot camps, which use Java to teach OOP, data structures, algorithms and more. Java prepares career changers well for developer roles.
Software Professionals
Both new and experienced software engineers regularly learn new Java skills to build production-grade systems. Its versatility means there's always more Java knowledge to absorb, from frameworks to best practices.
While younger learners can start with Java for foundational computer science knowledge, Java skills remain highly valuable even for senior professionals.
Core Java Concepts
Learning Java end-to-end takes time, but certain concepts form the crux. Beginners should focus on grasping these first:
Object-Oriented Programming
OOP is central to Java, so understanding classes, objects, inheritance, encapsulation and polymorphism is vital. All code centers around creating objects from predefined classes.
Data Types
Java has a variety of primitive (int, boolean, char etc.) and reference data types (e.g., String). Choosing appropriate types to represent data is key to writing efficient Java code.
Variables and Operators
Variables store data values, and operators manipulate them. Core operators involve arithmetic, assignment, comparison and logical operations. Mastering these basic building blocks enables complex logic.
Control Flow Statements
Control flow statements like if-else, switch, while and for loops control the order of execution. They allow non-linear code logic to solve more advanced problems.
Arrays & Collections
Arrays and collections like ArrayList store reference data types for efficient access. Collections are foundation of data structures like lists, maps and sets.
Methods
Methods group Java code for reuse and abstraction. Key techniques like overloading, overriding and passing arguments build modular, scalable software.
Classes & Objects
Classes define custom reference types and data structures. Instantiating class objects allows flexible, reusable components fundamental to OOP.
Inheritance
Inheritance defines parent-child class relationships, enabling child classes to inherit methods and properties from parents. This builds class hierarchies and reduces code duplication.
While this foundation isn't everything, it empowers learners to start applying Java to build functional programs.
How Long Does it Take?
How long it takes to learn Java depends greatly on your prior coding experience and learning style:
Beginners
For total beginners, learning core Java can take around 6 months of consistent practice. This assumes starting from zero programming knowledge to gain competency with Java fundamentals.
Experienced Developers
Experienced coders with backgrounds in C, Python or other languages can pickup Java more rapidly. Allow 3 months for an intermediate developer to adopt Java's syntax, OOP model and unique quirks.
Java Certifications
Those preparing for Associate or Professional Java certifications require 2-3 months per exam based on experience level. Certifications validate broad Java skillsets to employers.
Note effective Java learning requires both comprehending concepts and applying them through labs and projects. Learning with real examples accelerates progress.
While a significant time investment, Java unlocks abundant technical and career opportunities. The skills gained serve learners for years to come.
Key Java Applications
Once familiar with basic Java, exploring real-world uses cases helps cement knowledge. Here are some of the top applications of Java today:
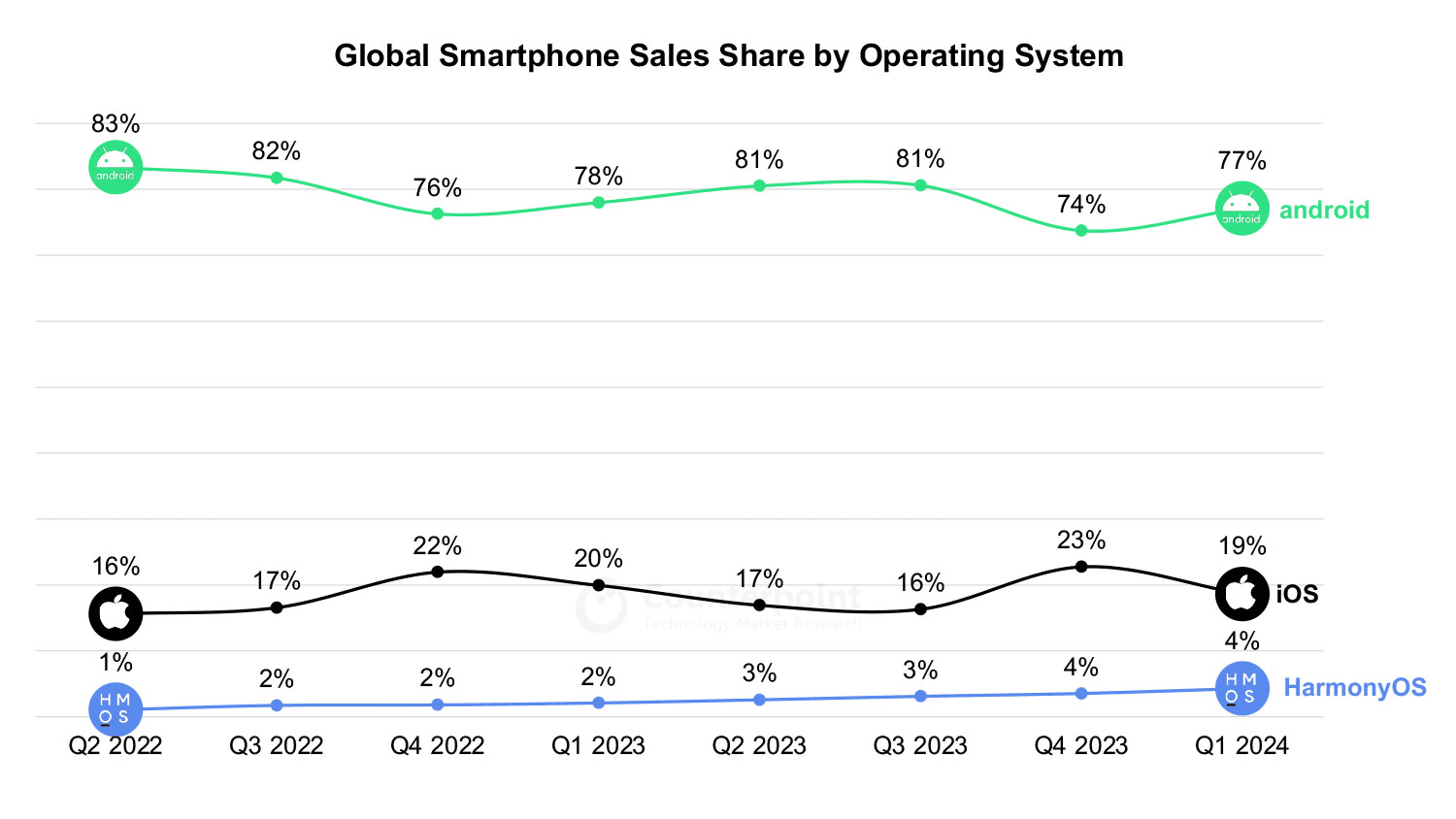
1. Android App Development
With 77% market share, Android is the dominant mobile OS making Java the de facto language for mobile dev. Developers build responsive UIs and complex app logic fueled by Java libraries and frameworks.
2. Enterprise Software
Java EE and the Spring framework power robust enterprise systems. Java enables high-volume transaction processing while integrating legacy systems across large organizations.
3. Big Data Analytics
Java stream processing frameworks like Apache Spark process petabytes of data for analytics. Hadoop ecosystem components utilize Java to structure and query huge datasets in distributed systems.
4. Scientific Computing & AI
Java runs complex physics, biology and chemistry simulations leveraging its fast runtime and rich ML libraries. It also trains deep learning models that power modern AI apps and tools.
5. High Frequency Trading
Java performance and versatility drive complex trading systems that exploit market opportunities in milliseconds. Java keeps up with the blistering speeds of HFT markets.
6. IoT & Embedded Systems
Java's hardware integration and real-time performance allow IoT devices to sense, process and actuate. It manages connectivity constraints of embedded devices like medical equipment.
These applications showcase Java’s immense capabilities today. Both new and seasoned developers have much to gain by advancing their Java skills.
Getting Started with Java
Here are helpful resources for those looking to start learning Java:
Online Courses
Structured online courses like Udemy and Coursera offer affordable, beginner-friendly Java instruction. These balance concepts with practical exercises at your own pace.
Books & Docs
Head First Java and Effective Java provide great book introductions. Official Java docs detail latest features and libraries for reference.
Bootcamps
Coding bootcamps offer intensive, accelerated Java training through instructor-led cohorts. These prepare learners for developer roles in months.
Java Community
Active forums like r/JavaHelp offer customized answers to development roadblocks. The Java community shares hard-earned knowledge.
Pet Projects
Applying Java to build personal projects reinforces skills with direct experience. Start small then expand scope over time.
Conclusion
Java has earned its reputation as a versatile, powerful programming language well worth the effort to learn. Whether just starting out or a seasoned professional, Java unlocks new career opportunities across virtually every technology domain.
It does require commitment – potentially 6 months for beginners to learn fundamentals. But Java fluency pays dividends across devices, platforms and industries. Through its vibrant community and wealth of learning materials, anyone willing can unlock the possibilities of Java.
Share this
Contributor
Staff
The team of expert contributors at Businessabc brings together a diverse range of insights and knowledge from various industries, including 4IR technologies like Artificial Intelligence, Digital Twin, Spatial Computing, Smart Cities, and from various aspects of businesses like policy, governance, cybersecurity, and innovation. Committed to delivering high-quality content, our contributors provide in-depth analysis, thought leadership, and the latest trends to keep our readers informed and ahead of the curve. Whether it's business strategy, technology, or market trends, the Businessabc Contributor team is dedicated to offering valuable perspectives that empower professionals and entrepreneurs alike.
previous
3 Common Warehouse Problems and How to Solve Them
next
The Vital Role of Factory Audit Services in Enhancing Risk Management