business resources
Chainlink vs. Polkadot: Which Blockchain Network Offers Better Scalability?
7 Feb 2025, 0:35 pm GMT
Chainlink vs. Polkadot
Scalability is the key to blockchain's future, and two networks—Chainlink and Polkadot—are leading the charge with unique solutions. Which network truly offers better scalability? Read on to discover which platform aligns best with your blockchain goals!
Table of contents:
- Introduction
- Understanding Scalability in Blockchain Networks
- What is Chainlink, the scalability feature and how does it work?
- What is Polkadot, the scalability feature and how does it work?
- Key differences between ?hainlink and Polkadot
- Polkadot vs. Chainlink: Comparison
- Conclusion
Blockchain technology has seen significant advancements, with various networks emerging to address critical challenges such as scalability, interoperability, and security. Among the most prominent projects in the space are Chainlink vs. Polkadot, each designed with unique approaches to solving different blockchain issues.
Scalability remains one of the most discussed topics in blockchain development, determining how efficiently a network can process transactions and support a growing user base.
In a podcast interview with Dinis Guarda, Bill Laboon, the Head of Education and Grants at the Web3 Foundation, explains the features of decentralised systems:
“Polkadot makes our system very autonomous, that’s very democratic as well as powerful. So, we get the many benefits of centralized decision making without having a centralized decision maker, where our system allows us to evolve. If we feel that our system is not meeting our needs, we really can vote in for a new system”, he said.
Understanding scalability in blockchain networks
Scalability in blockchain networks refers to their ability to handle an increasing number of transactions without compromising speed, security, or efficiency. Traditional blockchain networks, such as Bitcoin and Ethereum, face significant scalability challenges due to their consensus mechanisms and block size limitations. Solutions such as layer-2 scaling, sharding, and cross-chain communication are used to address these issues.
Both Chainlink vs. Polkadot employ different strategies to enhance scalability, making them viable options for various blockchain applications.
What is Chainlink and the scalability feature?
Chainlink is a decentralised oracle network that enables smart contracts to interact with real-world data, APIs, and external blockchains. It was developed to bridge the gap between on-chain and off-chain data, ensuring accurate and tamper-proof information transfer.
Scalability features of Chainlink
Chainlink’s approach to scalability is distinct from conventional blockchain networks. Instead of focusing on increasing transaction throughput on a single chain, Chainlink enhances the efficiency of smart contracts by providing access to off-chain resources. Some key scalability solutions in Chainlink include:
- Decentralised Oracle Networks (DONs) – Chainlink operates a network of independent oracles that collect and verify real-world data before feeding it into blockchain-based smart contracts.
- Data Providers – External data sources (such as market prices, weather conditions, and event outcomes) are integrated into Chainlink’s system to supply accurate information to smart contracts.
- Node Operators – Chainlink nodes retrieve data from external sources, process it, and relay it to smart contracts. Operators stake LINK tokens as a security measure to ensure data integrity.
- Smart Contract Integration – Chainlink’s oracle services are used by blockchain applications for decentralised finance (DeFi), supply chain management, insurance, and gaming.
- Off-Chain Computation – Chainlink enhances scalability by allowing complex computations to be performed off-chain, reducing the processing burden on blockchain networks.
- LINK Token – The native utility token of Chainlink, used to pay node operators for retrieving, processing, and delivering data to smart contracts.
What is Polkadot and the scalability feature?
Polkadot is a multi-chain blockchain network designed to enhance interoperability, scalability, and security across different blockchain ecosystems. Developed by the Web3 Foundation, Polkadot allows multiple blockchains, called parachains, to operate simultaneously while being connected to a central Relay Chain.
Scalability features of Polkadot
Polkadot employs a unique sharded architecture, enabling multiple chains to process transactions in parallel. Below are its core components:
- Relay Chain – The backbone of Polkadot, responsible for network security, consensus, and cross-chain communication. It connects and coordinates parachains.
- Parachains – Independent blockchains that run alongside the Relay Chain. Each parachain has its own features and functionalities but benefits from Polkadot’s shared security and scalability.
- Parathreads – Similar to parachains but operate on a pay-as-you-go model, allowing smaller projects to access Polkadot’s network without leasing a full parachain slot.
- Bridges – Allow interoperability with other blockchain networks, including Ethereum and Bitcoin.
- Consensus Mechanism (NPoS) – Polkadot uses Nominated Proof-of-Stake (NPoS), where validators secure the network, while nominators stake DOT tokens to support trusted validators.
Key differences between Chainlink and Polkadot
Despite both being innovative blockchain solutions, Chainlink vs. Polkadot differ significantly in their scalability approaches. Below is a detailed examination of the key differences:
- Core functionality:
- Chainlink functions as a decentralised oracle network, which means it enables smart contracts to securely interact with external data sources, APIs, and off-chain computations. It primarily focuses on enhancing the functionality of smart contracts by ensuring reliable data inputs.
- Polkadot, on the other hand, is a multi-chain framework that facilitates interoperability between different blockchains. It allows different networks to communicate and share information efficiently, making it ideal for creating a decentralised internet of blockchains.
- Scalability model:
- Chainlink improves scalability by reducing on-chain computation. It achieves this by utilising decentralised oracles that fetch and verify off-chain data before transmitting it to smart contracts. This reduces the workload on the blockchain and enhances the efficiency of decentralised applications (dApps).
- Polkadot’s scalability is achieved through its parachain architecture, where multiple blockchains run in parallel and process transactions independently. This significantly increases the network’s overall capacity without overloading a single blockchain.
- Transaction throughput:
- Polkadot’s parachains allow for parallel transaction processing, which increases the network’s ability to handle a higher volume of transactions at a given time. This results in a high throughput compared to single-chain networks.
- Chainlink does not focus on increasing the number of transactions processed per second. Instead, it optimises smart contract execution by ensuring that external data is efficiently and securely processed before it reaches the blockchain.
- Use cases:
- Chainlink is widely used for DeFi (Decentralised Finance), insurance, gaming, and supply chain applications where accurate external data is required. It is the preferred choice for projects that need tamper-proof real-world data.
- Polkadot is designed for interoperability, blockchain development, and decentralised application deployment. It provides a framework where developers can create custom blockchains (parachains) tailored to specific use cases.
- Consensus mechanism:
- Chainlink relies on external validators and a staking model to ensure the accuracy and reliability of the data provided by oracles. Oracles are incentivised through LINK token rewards to maintain data integrity.
- Polkadot employs a Nominated Proof-of-Stake (NPoS) consensus mechanism, where validators and nominators are responsible for securing the network and processing transactions. This model enhances security while ensuring decentralisation.
Polkadot vs. Chainlink: Comparison
To determine which blockchain network offers better scalability, it is essential to compare their features across various aspects:
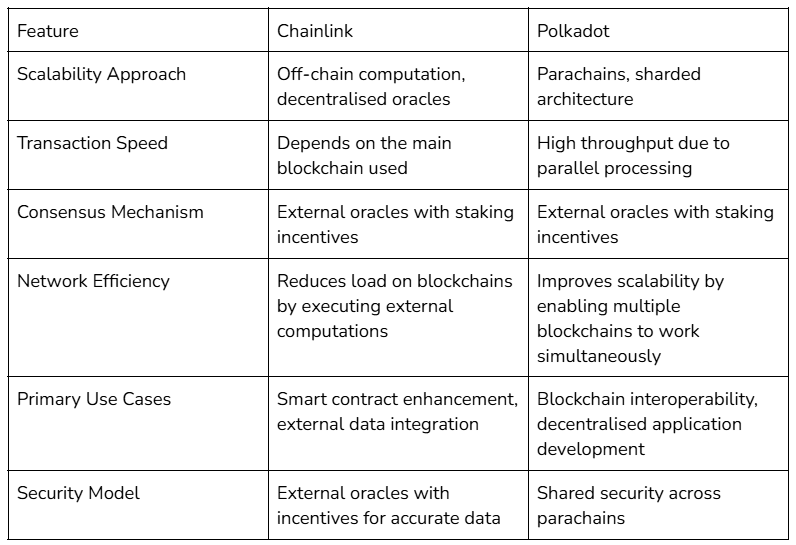
Which blockchain network offers better scalability?
Scalability is key in blockchain networks, ensuring they handle growing transactions efficiently. Polkadot and Chainlink enhance scalability differently due to their unique roles.
1. General blockchain scalability (Polkadot)
Polkadot's multi-chain architecture enables parallel transaction processing across parachains, preventing congestion seen in single-chain networks. Its Relay Chain provides shared security, reducing overhead and improving efficiency. Cross-Chain Message Passing (XCMP) enhances interoperability, ensuring seamless communication between chains. Polkadot achieves high throughput, handling 1,000 TPS on the relay chain and scaling beyond 100,000 TPS with parachains, making it highly scalable.
2. Oracle network scalability (Chainlink)
Chainlink is a decentralised oracle network, improving smart contract scalability by providing efficient off-chain data. Off-Chain Reporting (OCR) reduces blockchain congestion by aggregating data before submission. Decentralised Oracle Networks (DONs) distribute computational loads, and Layer-2 integrations reduce transaction costs, supporting high-frequency applications.
Related Contents:
Share this
Pallavi Singal
Editor
Pallavi Singal is the Vice President of Content at ztudium, where she leads innovative content strategies and oversees the development of high-impact editorial initiatives. With a strong background in digital media and a passion for storytelling, Pallavi plays a pivotal role in scaling the content operations for ztudium's platforms, including Businessabc, Citiesabc, and IntelligentHQ, Wisdomia.ai, MStores, and many others. Her expertise spans content creation, SEO, and digital marketing, driving engagement and growth across multiple channels. Pallavi's work is characterised by a keen insight into emerging trends in business, technologies like AI, blockchain, metaverse and others, and society, making her a trusted voice in the industry.
previous
What to Know About Non-Compete Agreements
next
3 Ways QR Codes Enhance Digital Security