business resources
Chainlink vs Solana: Which Blockchain Has More Real-World Utility?
12 Feb 2025, 6:52 am GMT
Chainlink vs Solana: Which Blockchain Has More Real-World Utility?
Chainlink secures $40B+ in smart contract value with its decentralised oracles, powering DeFi and enterprises. Meanwhile, Solana processes 65,000 transactions per second with near-zero fees, driving Web3 adoption. Which offers greater real-world utility? Let’s dive in!
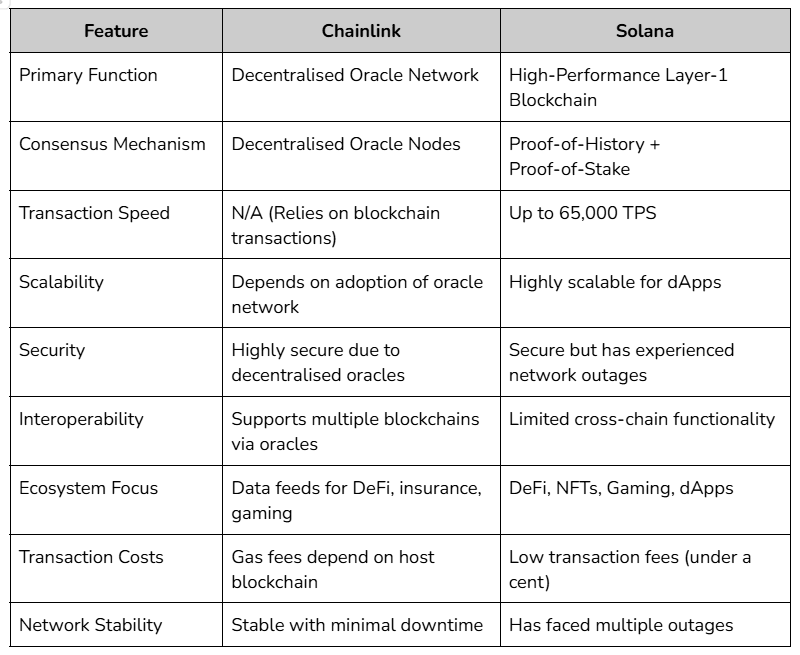
Chainlink and Solana are two prominent blockchain-based solutions with distinct purposes. While Chainlink focuses on decentralised oracles and data connectivity, Solana is a high-performance blockchain aimed at scalability and speed.
As of early 2025, the blockchain industry continues to evolve with projects like Chainlink and Solana playing pivotal roles. Chainlink (LINK) has demonstrated significant growth, with a market capitalisation exceeding $16 billion and a daily trading volume surpassing $1.4 billion. In a recent performance, Chainlink surged by 31% over a seven-day period, nearly matching Solana's 35% gain during the same timeframe.
Solana (SOL), known for its high throughput and low transaction costs, has also seen substantial market activity, with its price reaching $176.96 and a market cap of $85.7 billion as of January 13, 2025.
Both projects have been recognised in Grayscale's Top 20 Crypto List for Q1 2025, highlighting their prominence in the digital asset landscape.
This article provides an in-depth comparison of Chainlink vs Solana, covering their architecture, use cases, technological differences, and market adoption.
Read this article: Chainlink vs. Polkadot: Which Blockchain Network Offers Better Scalability?
Understanding Chainlink and Solana
What is Chainlink?
Chainlink is a decentralised oracle network designed to bridge the gap between blockchain-based smart contracts and real-world data. Smart contracts, which are self-executing agreements with the terms directly written into code, require accurate and reliable external data to function effectively. However, blockchains themselves are inherently closed systems, meaning they cannot natively access data from external sources. This is where Chainlink comes into play.
Chainlink’s primary function is to provide tamper-proof, real-world data to smart contracts on various blockchains. It achieves this through a network of decentralised oracles, which are nodes that fetch, validate, and deliver data from off-chain sources to on-chain smart contracts. By ensuring data integrity and reliability, Chainlink enables smart contracts to execute complex functions that depend on external information, such as price feeds, weather data, or sports results.
Key Features of Chainlink
- Decentralised Oracles: Chainlink allows smart contracts to securely interact with external data sources.
- Verifiable Randomness Function (VRF): Provides provably fair random number generation for blockchain applications, particularly in gaming and NFTs.
- Cross-Chain Interoperability: Supports multiple blockchains through the Chainlink Cross-Chain Interoperability Protocol (CCIP).
- Security and Reliability: Utilises multiple data providers to prevent single points of failure.
What is Solana?
Solana, on the other hand, is a high-performance blockchain platform designed to support decentralised applications (dApps) and cryptocurrencies. Launched in 2020, Solana has quickly gained recognition for its scalability, speed, and low transaction costs. These attributes make it an attractive option for developers looking to build and deploy dApps that require high throughput and minimal latency.
At the core of Solana’s architecture is its unique consensus mechanism, known as Proof of History (PoH). Unlike traditional Proof of Work (PoW) or Proof of Stake (PoS) systems, PoH introduces a cryptographic clock that timestamps transactions before they are added to the blockchain. This innovation allows Solana to process transactions in parallel, significantly increasing its throughput. In fact, Solana boasts a theoretical capacity of 65,000 transactions per second (TPS), far surpassing many of its competitors.
Key features of Solana
- Proof-of-History (PoH): A unique consensus mechanism that timestamps transactions, enhancing processing efficiency.
- High Throughput: Solana can process over 65,000 transactions per second (TPS), making it one of the fastest blockchains.
- Low Transaction Costs: Fees on Solana are significantly lower than on many other blockchain networks.
- Developer-Friendly Environment: Supports Rust and C programming languages for building dApps.
Chainlink vs Solana: Key differences
While both Chainlink and Solana operate within the blockchain space, they serve fundamentally different purposes. Chainlink is primarily focused on providing decentralised oracle services, enabling smart contracts to interact with real-world data. Solana, in contrast, is a blockchain platform designed to support the development and deployment of decentralised applications.
1. Purpose and functionality
Chainlink’s primary function is to act as a bridge between blockchains and external data sources. Its decentralised oracle network ensures that smart contracts have access to accurate and reliable information, which is essential for their execution. Without Chainlink, many smart contracts would be unable to perform their intended functions, particularly those that rely on real-world data.
Solana, on the other hand, is a full-fledged blockchain platform that provides the infrastructure for building and running decentralised applications. Its high throughput, low latency, and low transaction costs make it an ideal choice for developers looking to create scalable and efficient dApps.
2. Technology and architecture
Chainlink’s technology revolves around its decentralised oracle network. It uses a combination of on-chain and off-chain components to fetch, validate, and deliver data to smart contracts. The network’s decentralised nature ensures that the data provided is secure, reliable, and resistant to manipulation.
Solana’s technology, meanwhile, is centred around its Proof of History consensus mechanism. By introducing a cryptographic clock, Solana is able to process transactions in parallel, significantly increasing its throughput. Additionally, Solana’s architecture is designed to minimise latency and reduce transaction costs, making it one of the fastest and most efficient blockchains in existence.
3. Use cases
Chainlink’s use cases are primarily focused on enabling smart contracts to interact with real-world data. This includes applications in decentralised finance (DeFi), insurance, supply chain management, and more. For example, in the DeFi space, Chainlink’s price feeds are used to determine the value of assets and execute trades, while in insurance, its oracles can provide data on weather conditions or other external events that trigger payouts.
Solana’s use cases, on the other hand, are more diverse, given its role as a blockchain platform. It supports a wide range of applications, including decentralised exchanges (DEXs), gaming platforms, non-fungible token (NFT) marketplaces, and more. Solana’s high throughput and low fees make it particularly well-suited for applications that require fast and cost-effective transactions, such as high-frequency trading or in-game purchases.
4. Ecosystem and adoption
Chainlink has established itself as a critical component of the blockchain ecosystem, with its oracles being integrated into numerous projects across various blockchains. Its partnerships with leading companies and blockchain platforms have further solidified its position as the go-to solution for decentralised oracle services.
Solana, while relatively new compared to Chainlink, has seen rapid adoption and growth. Its ecosystem now includes a wide range of dApps, protocols, and projects, many of which have gained significant traction. Solana’s ability to support high-performance applications has attracted developers and users alike, contributing to its growing popularity.
Read this article: Chainlink vs XRP: Which Crypto Has Better Adoption in Finance & DeFi?
Chainlink vs Solana: A holistic comparison
Complementary roles in the blockchain ecosystem
It is important to note that Chainlink and Solana are not direct competitors; rather, they serve complementary roles within the blockchain ecosystem. Chainlink’s decentralised oracle services can be integrated with Solana’s blockchain, enabling smart contracts on Solana to access real-world data. This synergy between the two projects highlights the collaborative nature of the blockchain space, where different technologies work together to create a more robust and functional ecosystem.
For example, a decentralised exchange built on Solana could use Chainlink’s price feeds to ensure accurate and up-to-date pricing information. Similarly, a supply chain management application on Solana could leverage Chainlink’s oracles to track and verify the movement of goods in real-time. By combining the strengths of both platforms, developers can create more sophisticated and reliable applications.
Final thoughts
Chainlink and Solana represent two distinct but equally important facets of the blockchain ecosystem. Chainlink’s decentralised oracle network provides a critical service by enabling smart contracts to interact with real-world data, while Solana’s high-performance blockchain platform offers a scalable and efficient infrastructure for building decentralised applications.
While their purposes and functionalities differ, both projects contribute to the broader goal of creating a more decentralised and interconnected world. As the blockchain space continues to evolve, the collaboration between projects like Chainlink and Solana will play a crucial role in driving innovation and adoption.
Ultimately, the choice between Chainlink and Solana depends on the specific needs and objectives of a project. For those seeking to enhance the functionality of smart contracts with real-world data, Chainlink is the clear choice. For developers looking to build high-performance decentralised applications, Solana offers a compelling solution. Together, these projects exemplify the diversity and potential of blockchain technology, paving the way for a more decentralised future.
Related Contents:
Share this
Pallavi Singal
Editor
Pallavi Singal is the Vice President of Content at ztudium, where she leads innovative content strategies and oversees the development of high-impact editorial initiatives. With a strong background in digital media and a passion for storytelling, Pallavi plays a pivotal role in scaling the content operations for ztudium's platforms, including Businessabc, Citiesabc, and IntelligentHQ, Wisdomia.ai, MStores, and many others. Her expertise spans content creation, SEO, and digital marketing, driving engagement and growth across multiple channels. Pallavi's work is characterised by a keen insight into emerging trends in business, technologies like AI, blockchain, metaverse and others, and society, making her a trusted voice in the industry.
previous
Education In Society 5.0: Balancing Technology, Equity, And Lifelong Learning
next
Chainlink vs Avalanche: Comparing Their Growth Potential & Market Trends