business resources
Chainlink vs Avalanche: Comparing Their Growth Potential & Market Trends
12 Feb 2025, 7:21 am GMT
Chainlink vs Avalanche: Comparing Their Growth Potential & Market Trends
The blockchain race heats up as Chainlink, securing $40B+ in smart contract value, powers DeFi with reliable oracles, while Avalanche, handling 4,500 TPS, fuels dApp scalability with low fees. With institutional adoption rising and Web3 expanding, which has greater growth potential in 2025?
The blockchain industry has experienced significant innovation over the past decade, leading to the emergence of multiple platforms that serve different purposes. Chainlink and Avalanche are two widely recognised projects in the decentralised ecosystem, each addressing specific challenges in blockchain technology.
Chainlink is a decentralised oracle network that enables smart contracts to interact with real-world data, while Avalanche is a high-performance blockchain platform designed for scalability and decentralised applications (dApps).
The total market capitalisation of the blockchain industry reached over $2 trillion in 2021, demonstrating its rapid growth. As of 2024, Chainlink (LINK) holds a market capitalisation of approximately $8 billion, while Avalanche (AVAX) has a market capitalisation of around $10 billion.
This article presents a detailed comparison of Chainlink vs Avalanche, analysing their core functions, architecture, use cases, and overall impact on the blockchain industry.
Read this article: Chainlink vs Polkadot: Which Blockchain Network Offers Better Scalability?
Overview of Chainlink
Chainlink is a decentralised oracle network that connects blockchain-based smart contracts with off-chain data sources. It addresses the limitation of smart contracts, which are unable to directly access external information such as financial market prices, weather data, or sports results.
Chainlink was founded by Sergey Nazarov in 2017 and has since grown into one of the most widely used oracle networks. It allows smart contracts to fetch reliable and tamper-proof data, making it a crucial component for decentralised finance (DeFi), gaming, and other blockchain-based applications.
Key features of Chainlink
- Decentralised Oracles – Chainlink employs multiple independent oracle nodes to ensure the accuracy and reliability of external data.
- Smart Contract Integration – Developers can integrate Chainlink’s oracle services into Ethereum, Binance Smart Chain, and other blockchains.
- Verifiable Randomness – The Chainlink VRF (Verifiable Random Function) is used in gaming and NFT applications to generate provable randomness.
- Cross-Chain Connectivity – Chainlink facilitates interoperability between different blockchain networks, enabling seamless data transfer.
- Secure Data Feeds – Chainlink provides aggregated and decentralised price feeds for DeFi applications, ensuring transparency and accuracy.
Use cases of Chainlink
- Decentralised Finance (DeFi): Chainlink oracles supply financial market data to DeFi applications, enabling functions such as lending, borrowing, and derivatives trading.
- Gaming and NFTs: Chainlink VRF is used for fair randomness in blockchain-based games and NFT drops.
- Insurance and Prediction Markets: Smart contracts rely on Chainlink to verify events and process payouts accordingly.
- Enterprise Adoption: Traditional businesses use Chainlink to bring real-world data onto blockchain networks.
Overview of Avalanche
Avalanche is a blockchain platform designed to provide high throughput, low transaction fees, and customisable blockchain deployment. Launched in 2020 by Ava Labs, Avalanche aims to address scalability and interoperability challenges faced by existing blockchain networks.
Avalanche uses a unique consensus mechanism called the Avalanche consensus protocol, which enables high-speed transactions without compromising security or decentralisation. The platform supports multiple blockchains, allowing developers to create customised dApps and enterprise solutions.
Key features of Avalanche
- High scalability – Avalanche can process 4,500 transactions per second (TPS), significantly higher than many traditional blockchains.
- Subnets for custom blockchain creation – Developers can create independent blockchains using Avalanche Subnets, tailored to specific needs.
- Low transaction fees – Compared to Ethereum, Avalanche offers lower gas fees, making it cost-effective for developers and users.
- Interoperability – Avalanche supports cross-chain functionality, enabling communication with Ethereum and other blockchain networks.
- Security and decentralisation – The Avalanche consensus protocol ensures high security without sacrificing decentralisation.
Use cases of Avalanche
- Decentralised Finance (DeFi): Avalanche hosts numerous DeFi applications, offering fast and low-cost transactions for trading, lending, and borrowing.
- NFT and gaming ecosystem: The platform is used for NFT marketplaces and blockchain-based gaming applications.
- Enterprise solutions: Businesses leverage Avalanche’s Subnets to create private or consortium blockchains.
- Cross-chain bridges: Avalanche provides bridges to Ethereum and other networks, facilitating interoperability between ecosystems.
Read this article: Chainlink vs XRP: Which Crypto Has Better Adoption in Finance & DeFi?
Chainlink vs Avalanche: Key differences
While both Chainlink and Avalanche are integral to the blockchain ecosystem, they serve fundamentally different purposes. Chainlink is a middleware solution that enhances the functionality of smart contracts by providing external data, whereas Avalanche is a full-fledged blockchain platform designed to host dApps and digital assets. Below, we explore the key differences between the two projects.
1. Purpose and functionality
Chainlink’s primary focus is on data connectivity. It acts as a bridge between blockchains and the outside world, enabling smart contracts to interact with real-world information. This functionality is particularly crucial for DeFi applications, which rely on accurate and timely data for operations such as lending, borrowing, and trading.
Avalanche, in contrast, is a blockchain platform that provides the infrastructure for building and deploying decentralised applications. Its multi-chain architecture and high-performance consensus mechanism make it suitable for a wide range of use cases, from financial services to supply chain management.
2. Architecture
Chainlink operates as a network of decentralised nodes that fetch and deliver data to smart contracts. It does not have its own blockchain but instead integrates with existing blockchains like Ethereum, Binance Smart Chain, and Polygon. This interoperability is one of Chainlink’s greatest strengths, as it allows developers to leverage its oracle services across multiple platforms.
Avalanche, on the other hand, is a standalone blockchain platform with its own native token (AVAX) and ecosystem. Its multi-chain architecture enables it to support a variety of applications, from simple asset transfers to complex smart contracts. Additionally, Avalanche’s subnets feature allows developers to create custom blockchains tailored to specific use cases, further enhancing its versatility.
3. Consensus mechanism
Chainlink relies on the underlying blockchain’s consensus mechanism for security and validation. Its decentralised oracle network ensures data integrity by aggregating inputs from multiple nodes, but it does not have its own consensus protocol.
Avalanche, however, employs the Avalanche Consensus Protocol, which is designed for high throughput and low latency. This protocol uses a probabilistic approach to achieve consensus, enabling rapid transaction finality and scalability. As a result, Avalanche can handle a significantly higher volume of transactions compared to traditional blockchains.
4. Use cases
Chainlink’s use cases are primarily centred around data connectivity. It is widely used in DeFi for price feeds, in insurance for parametric triggers, and in gaming for verifiable randomness. Its ability to provide reliable and secure data makes it indispensable for applications that require real-world information.
Avalanche’s use cases are more diverse, given its role as a blockchain platform. It supports a wide range of applications, including decentralised exchanges, NFT marketplaces, and enterprise solutions. Its high performance and customisability make it an attractive option for developers looking to build scalable and efficient dApps.
Read this article: Chainlink vs Solana: Which Blockchain Has More Real-World Utility?
Comparison table: Chainlink vs Avalanche:
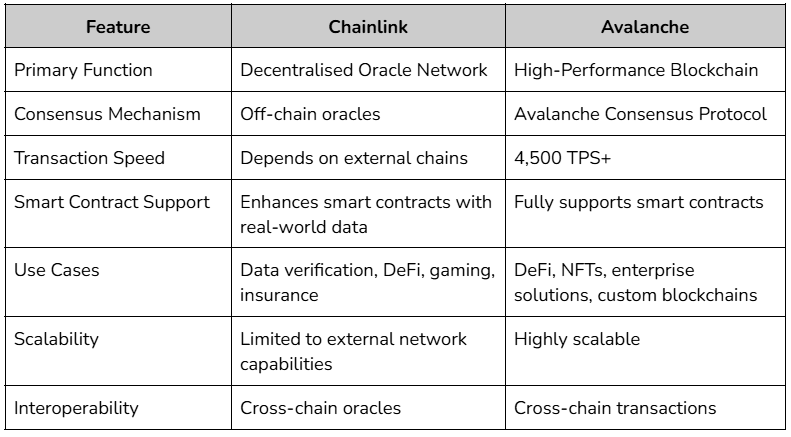
Complementary roles in the blockchain ecosystem
Despite their differences, Chainlink and Avalanche are not competitors; rather, they complement each other in the broader blockchain ecosystem. Chainlink’s oracle services can be integrated with Avalanche’s smart contracts, enabling developers to build sophisticated applications that leverage both platforms’ strengths. For example, a DeFi application built on Avalanche could use Chainlink’s price feeds to ensure accurate and reliable data for trading and lending operations.
This synergy highlights the collaborative nature of the blockchain space, where different projects work together to address various challenges and unlock new possibilities. As the ecosystem continues to evolve, the integration of Chainlink and Avalanche is likely to play a significant role in driving innovation and adoption.
Final thoughts
Chainlink and Avalanche represent two distinct but equally important facets of the blockchain ecosystem. Chainlink’s decentralised oracle network provides the critical infrastructure needed to connect smart contracts with real-world data, while Avalanche’s high-performance blockchain platform offers a scalable and efficient environment for building decentralised applications.
While their purposes and architectures differ, both projects contribute to the growth and maturation of the blockchain industry. By understanding their unique strengths and use cases, developers and enterprises can make informed decisions about how to leverage these technologies for their specific needs. As the blockchain space continues to expand, the collaboration between Chainlink and Avalanche is poised to unlock new opportunities and drive further innovation.
Related Contents:
Share this
Pallavi Singal
Editor
Pallavi Singal is the Vice President of Content at ztudium, where she leads innovative content strategies and oversees the development of high-impact editorial initiatives. With a strong background in digital media and a passion for storytelling, Pallavi plays a pivotal role in scaling the content operations for ztudium's platforms, including Businessabc, Citiesabc, and IntelligentHQ, Wisdomia.ai, MStores, and many others. Her expertise spans content creation, SEO, and digital marketing, driving engagement and growth across multiple channels. Pallavi's work is characterised by a keen insight into emerging trends in business, technologies like AI, blockchain, metaverse and others, and society, making her a trusted voice in the industry.
previous
Chainlink vs Solana: Which Blockchain Has More Real-World Utility?
next
The ultimate guide to buying IPTV. Everything you need to know