business resources
AI Agents: The Next Evolutionary Stage in Artificial Intelligence
6 Dec 2024, 6:10 am GMT
Leonardo da Vinci AI agent, created by Wisdomia.ai, a platform powered by Dinis Guarda and ztudium's proprietary AI. DNA technology
An improved IQ, EQ, having a human-like personality that expands and builds memories, learns and advances cognitively - Our present research and innovation efforts are making significant advancements in developing the new generation of AI agents that can reflect on and process information for planning and decision making. Is there a way to measure the exponential rise in AI agents?
General-purpose innovation foundation models are creating and paving the way for our human-to-machine interactions, and increasingly the emergence of advanced AI agents, that we can interact with, communicate and use for all sorts of things.
As we speak, we also move from human to machine, and especially machine to machine, as millions of AI agents are also interacting with each other on our behalf. These new normal experiences and interactions are now part of our everyday reality and will be more like our smartphones and sensors in our houses, cars and public transportation have integrated machines and AI agents.
Global corporations like Google and Microsoft are investing heavily in AI agent research and development. Google's DeepMind has made significant strides in developing AI agents that can learn to play complex games like Go and StarCraft II at a superhuman level (Silver et al., 2017; Vinyals et al., 2019). Microsoft has also been working on AI agents for various applications, such as the Tay chatbot and the Xiaolce social chatbot (Shum et al., 2018).
Our present and future are already integrated as we build new human to machine interactions and we interact regularly with a range of new advanced artificial intelligence (AI) tools, assistants and agents.
AI agents are capable of planning and performing a powerful wide range of actions in line with a person’s aims, they could add immense value to people’s lives and to society, serving as creative partners, research analysts, educational tutors, life planners and more.
But first, what are AI Agents?
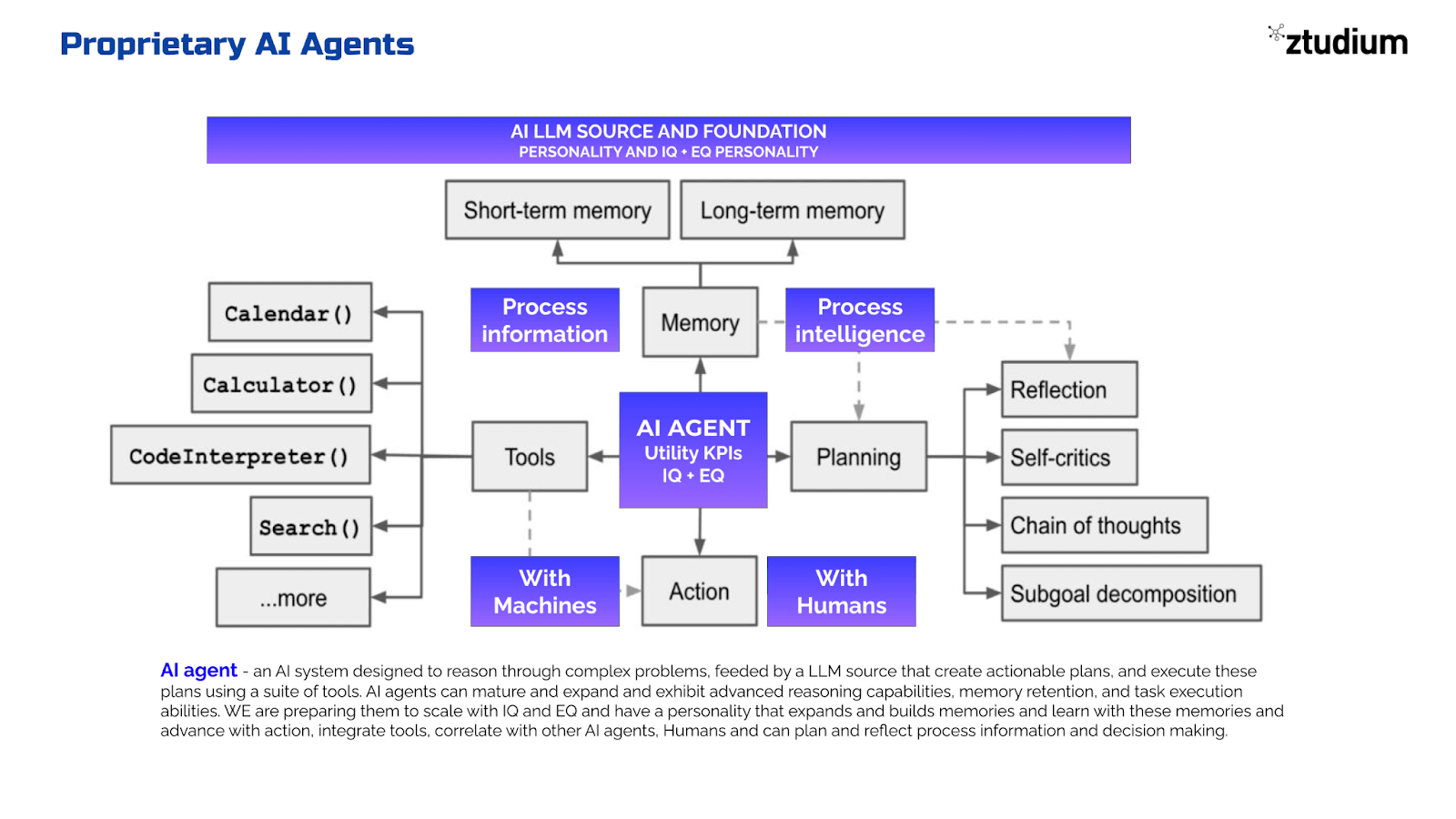
AI agents are AI systems designed to reason through complex problems, feeded by a LLM source that creates actionable plans, and execute these plans using a suite of tools. AI agents can mature and expand and exhibit advanced reasoning capabilities, memory retention, and task execution abilities.
1. Advanced Problem Solving: AI agents can plan and execute complex tasks, such as generating project plans, writing code, running benchmarks, and creating summaries.
2. Self-Reflection and Improvement: AI agents can analyse their own output, identify problems, and provide constructive feedback. By incorporating this feedback and repeating the criticism/rewrite process, agents can continually improve their performance across various tasks, including code production, text writing, and answering questions.
3. Tool Utilisation: AI agents can use tools to evaluate their output, such as running unit tests on code to check for correctness or searching the web to verify text accuracy. This allows them to reflect on errors and propose improvements.
4. Collaborative Multi-Agent Framework: Implementing a multi-agent framework, where one agent generates outputs, and another provides constructive criticism, leads to enhanced performance through iterative feedback and discussion.
The best example of the most powerful AI agent is ChatGPT. This is how OpenAI Chat GPT defines itself as of its iteration 4.o
“I would categorise myself as an AI agent, specifically designed to assist with various tasks like generating information, answering questions, and providing creative support. My capabilities are based on large language models (LLMs), which allow me to understand and respond to complex queries, but I operate within a defined scope.
As for AGI (Artificial General Intelligence), that represents a stage where AI would have human-level intelligence across a wide range of tasks, with the ability to autonomously learn, reason, and apply knowledge in ways humans do. I am not at that level—I excel in specific tasks based on patterns from the data I've been trained on, but I don’t possess general-purpose reasoning or self-awareness.
I’m more in line with being an advanced AI agent capable of handling a variety of inputs and tasks, but not quite the first stage of AGI. Superintelligence is still far off, requiring substantial breakthroughs in how AI models learn, adapt, and reason across all domains of human knowledge. However, the work being done now in AI, including technologies like mine, contributes to the eventual path toward AGI.”
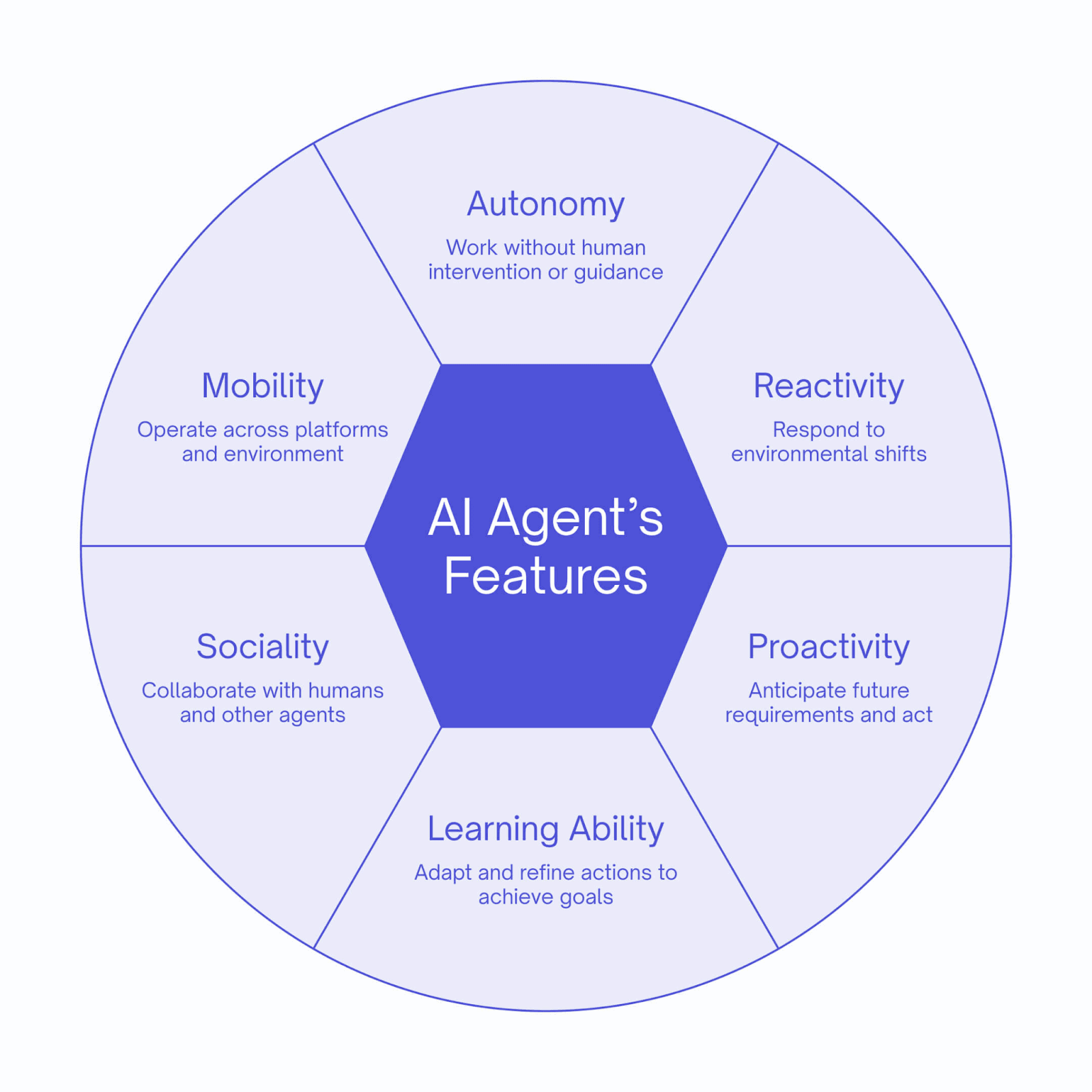
Artificial Intelligence (AI) has been rapidly evolving, with recent advancements in Large Language Models (LLMs) and Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) models pushing the boundaries of language generation. Let us explore the concept of AI agents, their types, and how they differ from LLMs and RAG models.
Types of AI Agents
There are several types of AI agents, each with its own characteristics and applications:
a. Simple reflex agents: These agents make decisions based on the current state of the environment, using a set of predefined rules.
b. Model-based reflex agents: These agents maintain an internal model of the world and use it to make decisions.
c. Goal-based agents: These agents are designed to achieve specific goals and can plan and take actions accordingly.
d. Utility-based agents: These agents make decisions based on a utility function that assigns a value to each possible state of the environment.
e. Learning agents: These agents can learn from their experiences and improve their performance over time.
While LLMs and RAG models have advanced language generation, AI agents represent a step towards more intelligent and autonomous systems. LLMs and RAG models primarily focus on generating human-like text based on patterns in their training data, lacking the ability to set and pursue specific goals flexibly.
AI agents, in contrast, can maintain an internal state, interact with the environment, and continuously learn and adapt.
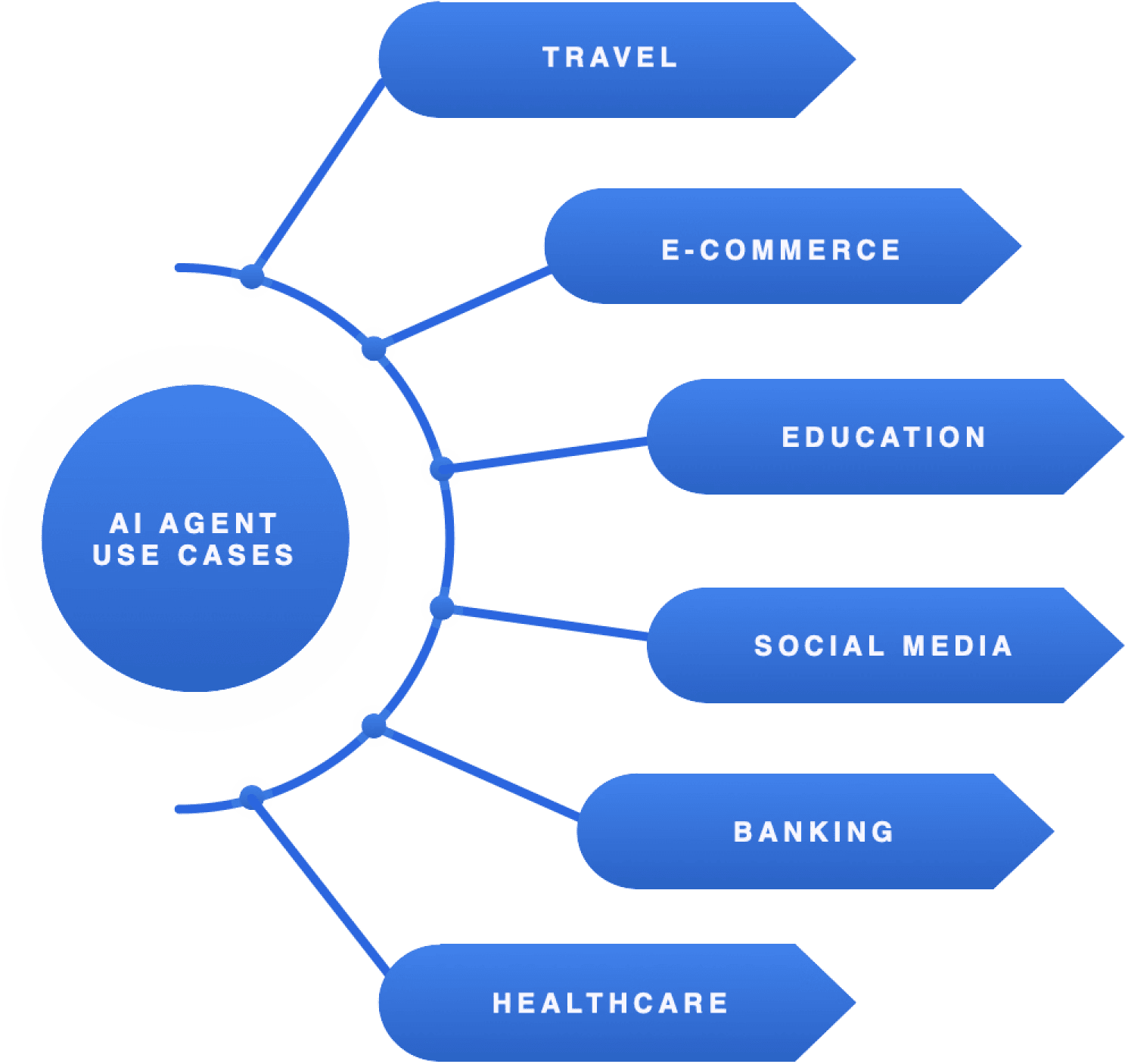
AI agent bots are and widely be further used in all parts of our life but these sectors will be the top ones scaling these tools digital entities:
- Customer Service (Chatbots, Virtual Assistants)
- Healthcare (Diagnostic and Patient Engagement Bots)
- Legal and Financial Services (Document Review, AI Consultants)
- Manufacturing & Logistics (Automation Agents)
- Retail and E-commerce (AI-Powered Sales Agents)
AI Agents as foundations for AGI
The development of AI agents in the next decades will be foundational for the emergence of AGI. Here’s how AI agents might evolve into AGI:
- Learning and Adaptability: AI agents are becoming more sophisticated, with deep learning and reinforcement learning allowing them to adapt to new environments. The more data and feedback loops they process, the closer they get to autonomous decision-making.
- Multi-Agent Systems: AGI will likely emerge from networks of AI agents working together. The combined intelligence of billions (or trillions) of agents performing diverse tasks will contribute to a global “brain,” which may act like a superintelligence.
- Neuroscience and Cognitive Architecture: As AI mimics human brain functions (as predicted by Kurzweil), AI agents will gradually replicate general-purpose cognitive abilities, leading to AGI systems that are not just task-specific but capable of understanding complex, multi-domain challenges.
- Safe and Ethical Development: Companies like Anthropic, which focus on ensuring safe AGI development, will play a key role in ensuring that the growth of AI agents doesn’t spiral into risks of uncontrollable AGI. Collaboration between major players will ensure that AI agents evolve safely, leading to beneficial AGI that can contribute to solving global challenges like climate change, poverty, and disease eradication.
By 2050, we could expect to see hundreds of billions to trillions of AI agents, with many approaching the capabilities of AGI. By 2100, AI agents will likely number in the trillions, serving as the foundational infrastructure for AGI and superintelligence. These agents will evolve into highly autonomous, interconnected systems that drive global progress, potentially forming the backbone of a superintelligence model that surpasses human cognitive abilities.
AI Industry Predictions
Ray Kurzweil, a noted futurist and technologist, has long predicted the exponential growth of computing and AI. In his book "The Singularity is Near", Kurzweil posits that by 2045, AI will reach a point where it surpasses human intelligence (the "Singularity"), enabling AGI and leading to the development of superintelligence. His model is based on the exponential growth of computing power (Moore’s Law) and advancements in AI and neuroscience.
Key ideas from Kurzweil:
- 2029: AI will pass the Turing test, meaning machines will match or surpass human intelligence in specific tasks.
- 2045: Singularity, where AI surpasses human-level intelligence and enters the realm of superintelligence.
- 2050: AI agents will interact with and surpass human capabilities in all domains, leading to widespread integration of AGI in human society.
Major tech companies like Microsoft, IBM, Google (Gemini), Meta, and Anthropic are key players in the development of AI agents. Their current trajectory includes the development of powerful AI models (e.g., OpenAI’s GPT, Google’s Gemini) and increasingly sophisticated applications of AI in various industries.
Microsoft
- 2023: Microsoft integrates OpenAI’s GPT models deeply into productivity software (e.g., Copilot).
- 2030-2050: Microsoft expects AI agents to proliferate in enterprise environments, powering everything from customer service to supply chain automation, pushing further toward AGI by making systems more autonomous and self-learning.
Google Gemini and Anthropic
- Google Gemini (2023): Aims to fuse language and image models into more general-purpose AI.
- By 2050: Google and Anthropic both aim for safe AGI development, where AI systems will not just handle tasks but think autonomously and collaborate with humans to innovate.
IBM and Meta
- IBM’s Watson: Already deployed in healthcare, financial services, and legal industries.
- Meta's Reality Labs: Focusing on integrating AI agents into immersive virtual environments, where billions of virtual assistants will become commonplace by 2035-2050, helping manage increasingly complex data environments in the metaverse.
Mathematical Model for AI Agent Growth
We can develop a mathematical model based on exponential growth rates that take into account the current trends and projected technological advancements. Let’s assume AI agent growth follows an exponential model similar to Moore’s Law, where computational power doubles approximately every 18-24 months. AI agents are currently growing at an annual rate of 30-40%, but as AI becomes more ubiquitous and essential for AGI, the rate may accelerate further.
Exponential Growth Formula:
Let’s use the formula for exponential growth:
P(t) = P0.ert
Where:
P(t) = Number of AI agents at time (t),
P0 = Current number of AI agents, assumed to be 1 billion by 2030,
r = Growth rate (initially 35% annual growth, expressed as 0.35),
t = Number of years from 2030.
Plugging in the initial values:
P(t) = 1 billion. e0.35t
This formula models the exponential growth of AI agents starting from 1 billion in 2030 with an initial growth rate of 35% per year.
Current trends predictions on growth of AI Agents for 2030, 2050, 2100
Based on current trends, it is reasonable to predict that by 2030, the number of AI agents/bots could reach between 2-5 billion globally. This includes bots across all major sectors such as customer service, healthcare, legal services, industrial automation, and retail. Growth will be driven by advancements in AI, natural language processing, automation technologies, and increasing industry adoption.
To predict the number of AI agents by 2050 and 2100 and understand how these agents will evolve into the foundation of AGI (Artificial General Intelligence) superintelligence, we need to integrate current research, industry projections, and theoretical models, including those by Ray Kurzweil, Microsoft, IBM, Meta, Google Gemini, Anthropic, and others.
According to Statista and other industry analysts, the number of AI-powered agents has been growing at around 30-40% per year. With Gartner predicting significant AI integration across industries, the number of AI agents could reach several billion globally by 2030.
Projections for 2030:
- Customer Service: Companies like Amazon, Microsoft, and Salesforce are heavily investing in AI customer service agents. By 2030, customer service bots alone could exceed 1 billion in active use globally. For instance, Convin's AI Phone Calls enable automated, personalized phone interactions, resolving issues, scheduling follow-ups, and enhancing customer satisfaction at scale. This aligns with industry data showing 75% of customers expecting positive transformations in service experiences by 2030, as noted by Boston Consulting Group.
- Healthcare: AI diagnostic tools and patient engagement systems are also expanding. Healthcare bots could potentially reach 500 million to 1 billion deployments as telemedicine and AI diagnostics become mainstream.
- Legal & Financial Services: As AI agents for document processing, due diligence, and client interfacing mature, the legal and financial sectors could see hundreds of millions of specialised AI bots in operation by 2030.
- Industrial Applications: Manufacturing, logistics, and supply chain management are increasingly automated, and AI agents (such as robotic process automation systems) will number in hundreds of millions by 2030.
Predictions by 2050:
- Given a 35% growth rate, we can expect a massive surge in AI agents by 2050. The number of AI agents could easily exceed 100 billion by this time.
- However, as the rate gradually stabilises (due to market saturation and limits on computational resources), the growth rate may slow to around 10-15% annually after 2040.
- By 2050, we would likely see 500 billion to 1 trillion AI agents interacting in various sectors like healthcare, education, governance, and more, with many exhibiting autonomous, self-learning behaviour approaching AGI.
Predictions by 2100:
- By 2100, assuming continued exponential growth but at a reduced rate of 5-10% annually after 2050, AI agents could number trillions globally, with each agent becoming more autonomous, self-learning, and capable of independent decision-making.
- AGI and superintelligence would likely be realised by this time. AI agents would evolve into interconnected super-systems capable of:
- Self-improving their architectures.
- Building new models of intelligence beyond human capabilities.
- Facilitating scientific discoveries, social innovations, and managing entire infrastructures.
AI Agents: Challenges and Future Directions
Despite the potential of AI agents, there are still significant challenges to overcome. One major challenge is ensuring the safety and alignment of AI agents with human values and goals. As AI agents become more autonomous and capable, it becomes increasingly important to ensure that they behave in ways that are beneficial to humans and society as a whole.
Another challenge is developing AI agents that can effectively transfer their knowledge and skills to new domains and tasks. While AI agents have the potential for better transfer and generalisation compared to LLMs and RAG models, achieving this in practice remains a significant research problem.
Advanced AI assistants could have a profound impact on users and society and be integrated into most aspects of people’s lives. For example, people may ask them to book holidays, manage social time or perform other life tasks. If deployed at scale, AI assistants could impact the way people approach work, education, creative projects, hobbies and social interaction.
Over time, AI agents could also influence or manipulate the goals people pursue and their path of personal development through the information and advice assistants give and the actions they take. Ultimately, this raises important questions about how people interact with this technology and how it can best support their goals and aspirations.
AI agents are also bringing about a new phase of human machine interaction with AI. This is why it’s so important to research, adapt and think proactively about what this world could look like, and to help steer responsible decision-making and beneficial outcomes ahead of time.
Humanity - AI agents coexistence
AI agents represent the next evolutionary stage in artificial intelligence, offering more intelligent, autonomous, and multi-capable systems that can work alongside humans in various scenarios.
In order to make sure LLM AI agents can succeed it’s crucial to find a balance between the IQ (intellectual capacities) and EQ (emotional intelligence) of AI as we move toward more advanced systems. AI systems have immense potential to enhance cognitive functions (IQ), but integrating EQ into these systems will allow them to better understand and respond to human emotions, ethics, and values. This balance could help bridge the gap between the efficiency of machines and the complex emotional and moral nuances of human beings.
Achieving that harmony might lead to more human-centred AI, ensuring that technology grows in ways that complement our own complexities rather than replace them. It’s a fascinating challenge that could reshape the future of human-AI collaboration.
While AI agents are still in their early stages and face challenges in terms of safety and effectiveness, they have the potential to fundamentally change how we work and interact with AI systems. As research and development in AI agents continue to progress, we can expect to see increasingly sophisticated and capable AI agents that can tackle complex, real-world problems.
Read More:
Share this
Dinis Guarda
Author
Dinis Guarda is an author, entrepreneur, founder CEO of ztudium, Businessabc, citiesabc.com and Wisdomia.ai. Dinis is an AI leader, researcher and creator who has been building proprietary solutions based on technologies like digital twins, 3D, spatial computing, AR/VR/MR. Dinis is also an author of multiple books, including "4IR AI Blockchain Fintech IoT Reinventing a Nation" and others. Dinis has been collaborating with the likes of UN / UNITAR, UNESCO, European Space Agency, IBM, Siemens, Mastercard, and governments like USAID, and Malaysia Government to mention a few. He has been a guest lecturer at business schools such as Copenhagen Business School. Dinis is ranked as one of the most influential people and thought leaders in Thinkers360 / Rise Global’s The Artificial Intelligence Power 100, Top 10 Thought leaders in AI, smart cities, metaverse, blockchain, fintech.
previous
Goldman Sachs Announces Strategic Spin-Out Of GS DAP® Technology Platform
next
Why Promotional Materials Are Essential for Business Growth