business resources
AI And Taxes: Global Case Studies With Benchmarks
10 Dec 2025, 7:30 am GMT
AI-driven tax administration worldwide shows strong gains in compliance, revenue, and efficiency. Case studies from the US, UK, Singapore, Australia, and major e-invoicing nations highlight that success relies on robust data integration, governance, real-time monitoring, and sustained investment in technology and human capability.
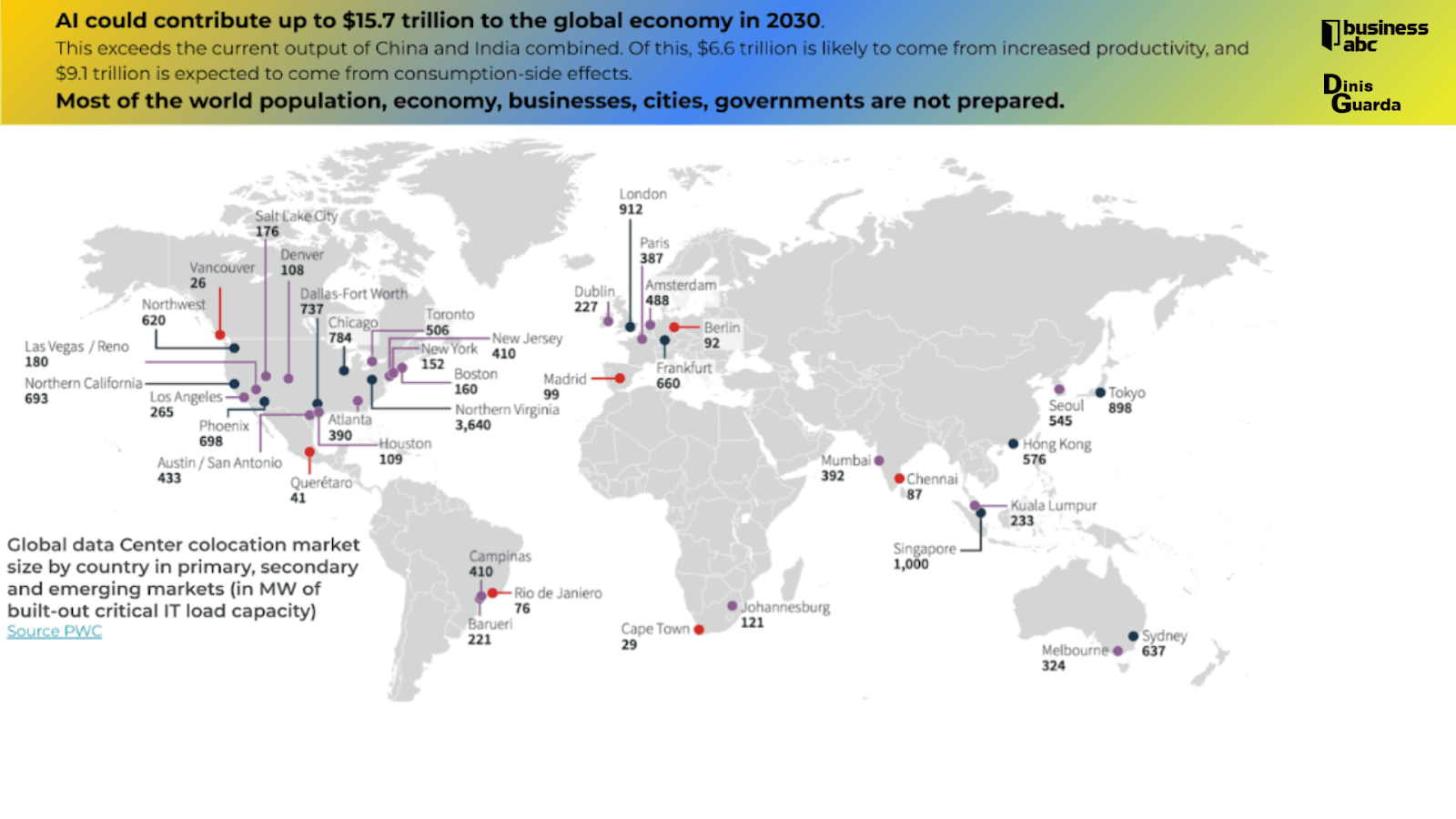
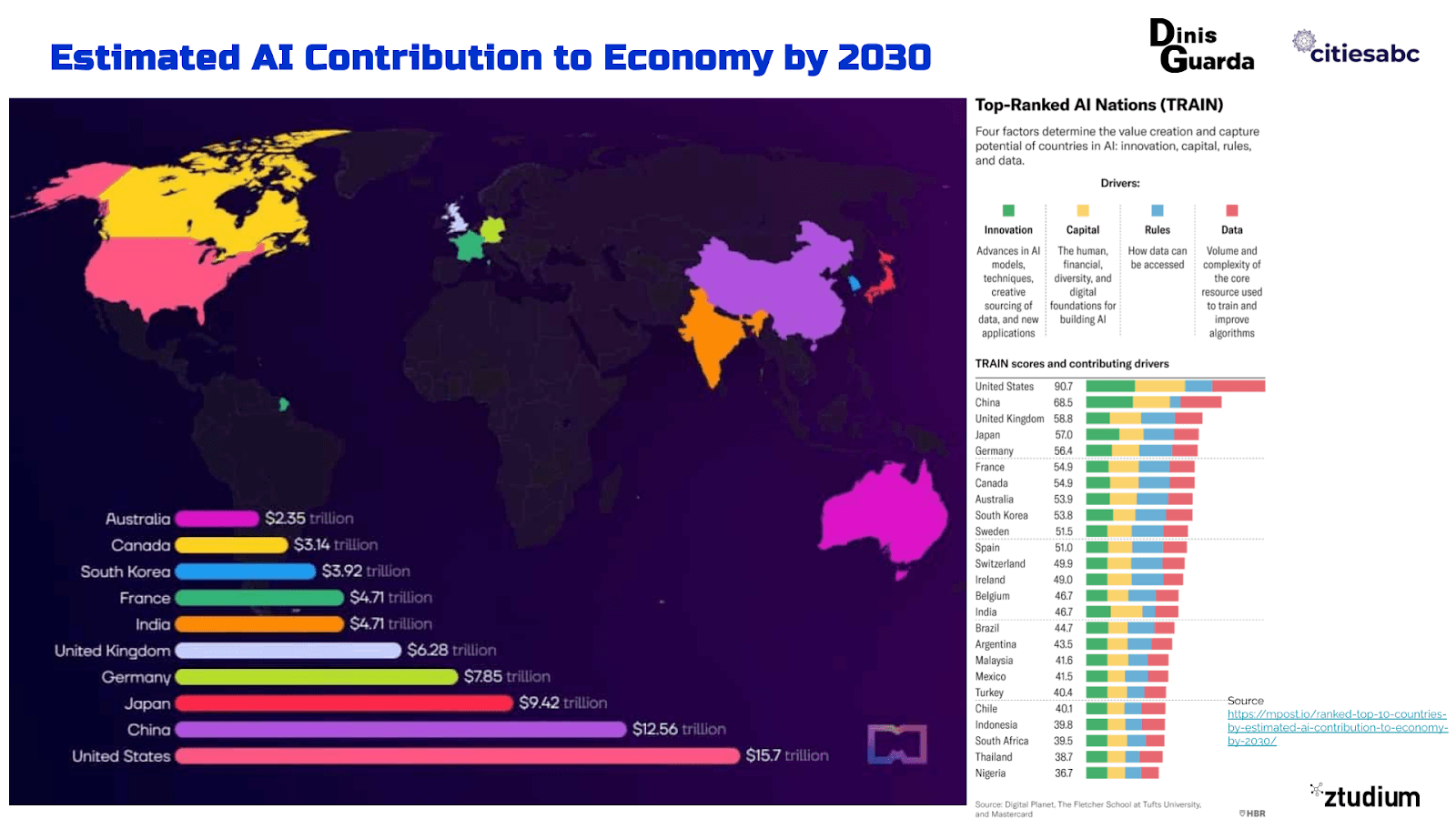
AI could be changing the world's social and economic landscape, and most studies and research estimate that it will contribute up to $15.7 trillion to the global economy by 2030.
Exceeds the combined current output of China and India. Of this, $6.6 trillion is likely to come from increased productivity, and $9.1 trillion is expected to come from consumption-side effects. Most of the world's population, economy, businesses, cities, and governments are not prepared. The governments will have to be prepared for this world innovation.
International experiences in AI-enhanced tax administration provide crucial insights into implementation strategies, performance outcomes, and governance frameworks that enable successful digital transformation. These case studies demonstrate practical approaches to common challenges whilst establishing performance benchmarks for different aspects of AI deployment.
A confluence of factors drives the race to build national sovereign AI infrastructure: Generative AI and Large Language Models (LLMs), escalating geopolitical and national security concerns, and companies such as NVIDIA’s aggressive expansion into the AI data centre market with its powerful GPU hardware and software stack that fuels the next generation of neoclouds.
As a result, “AI Factories” have emerged as a new class of digital infrastructure, attracting investment from governments, telecom operators, and other strategic players.
However, just as these GPU-based infrastructure projects are gaining momentum, the U.S. Bureau of Industry and Security (BIS) has introduced a new wave of proposed export rules known as the AI Diffusion Rules that are reshaping the global AI landscape.
Our latest Insight Note, “Navigating Risks and Opportunities in Sovereign AI Infrastructure,” explores these regulatory developments and their implications for AI Factory deployments, particularly in Tier 2 countries.
United States - Internal Revenue Service: Strategic Focus on Complex Entities
The IRS approach to AI deployment demonstrates the effectiveness of targeting high-complexity, high-value cases where traditional analysis methods prove insufficient. Their strategic focus on large partnerships and sophisticated business structures provides clear lessons for jurisdictions considering similar implementations.
The programme launched with AI-enhanced selection of complex large partnerships, opening audits of the 76 most extensive partnerships based on algorithmic risk assessment. This targeted approach concentrated resources on cases with the most significant revenue potential whilst building institutional expertise in AI-assisted enforcement. Results indicate hundreds of millions in additional assessments from early implementation phases.
Technical implementation employed ensemble methods combining multiple analytical approaches. Traditional statistical models provided baseline risk assessment, whilst machine learning algorithms identified non-linear patterns in financial relationships and transaction structures. Network analysis revealed connections between related entities that suggested coordinated tax planning activities.
The programme embeds AI into broader enforcement planning processes rather than operating as standalone analytical capability. Integration with case management systems, resource allocation processes, and strategic planning ensures that AI insights are effectively translated into operational improvements. This systematic integration proves essential for realising AI's full potential in enforcement applications.
Key lessons include starting with narrow, high-complexity segments where AI advantages are most apparent and pairing analysts with data scientists throughout the development and deployment process. Revenue agents provided essential domain expertise on tax avoidance techniques, while data scientists contributed technical skills in model development and validation. This collaborative approach ensured practical relevance whilst building institutional capability.
Performance measurement employs control groups and statistical testing to validate the effectiveness of AI systems. A comparison between AI-selected cases and traditional selection methods provides objective evidence of improvement, while identifying factors that influence performance variation across different taxpayer segments and case types.
United Kingdom - HMRC Connect: Enterprise Data Integration Excellence
HMRC's Connect programme represents comprehensive data integration spanning hundreds of sources to create holistic taxpayer profiles that enable sophisticated compliance monitoring and audit targeting. Launched in 2010, Connect demonstrates long-term commitment to data-driven tax administration with substantial performance improvements over more than a decade of operation.
The system integrates diverse data sources including banking information, property transactions, employment records, benefit payments, DVLA registrations, and various third-party reporting streams. This comprehensive integration creates 360-degree taxpayer profiles that reveal discrepancies impossible to detect through traditional audit methods.
Public estimates suggest billions in additional revenue recovery since Connect's launch, validating the investment in comprehensive data integration infrastructure. More importantly, Connect demonstrates that robust data foundations enable increasingly sophisticated analytical applications as technical capabilities evolve.
Technical architecture employs graph database technologies to model complex relationships between taxpayers, transactions, and third parties. Entity resolution algorithms handle the challenge of matching records across different systems despite variations in names, addresses, and identifiers. Machine learning models trained on integrated datasets achieve superior performance compared to single-source approaches.
The programme's governance framework ensures legal compliance whilst maximising analytical value. Data protection measures include purpose limitation, retention policies, and access controls that balance enforcement requirements with privacy protection. Regular legal review ensures continued compliance with evolving privacy and data protection requirements.
Key lessons emphasise building persistent entity-resolution capabilities and robust governance frameworks before implementing sophisticated analytical models. Connect's success required years of careful data integration, quality improvement, and governance development. The foundation of comprehensive, high-quality data proves essential for advanced AI applications.
Singapore - IRAS: Analytics-Driven Enforcement Excellence
Singapore's Inland Revenue Authority demonstrates systematic application of AI and advanced analytics to achieve substantial improvements in enforcement effectiveness whilst maintaining high service quality and procedural fairness standards.
The risk-based profiling system combines traditional compliance indicators with advanced analytical techniques including behavioural pattern recognition, network analysis, and predictive modeling. This comprehensive approach enables identification of compliance risks that would escape detection through traditional methods.
Performance results provide compelling evidence of analytical effectiveness. Corporate income tax audits selected through advanced analytics recovered approximately three times more revenue per case compared to random or qualitative selection methods during 2020-2023. This improvement demonstrates clear value from enhanced analytical capabilities whilst validating investment in AI infrastructure.
Technical implementation includes both supervised learning models trained on historical audit outcomes and unsupervised learning techniques that identify novel patterns potentially indicating emerging compliance risks. The system employs multiple model architectures optimised for different aspects of risk assessment whilst maintaining explainability requirements.
Experimental design includes random control cohorts that enable precise measurement of AI system performance improvements compared to traditional methods. This scientific approach provides objective evidence of programme effectiveness whilst identifying factors that influence performance across different case types and taxpayer segments.
Staff development programmes ensure effective human-AI collaboration through comprehensive training on analytical capabilities and limitations. Investment in human capital proves essential for realising full benefits from technological enhancement whilst maintaining professional judgment in complex cases.
Australia - ATO: Governance Framework Leadership
The Australian Taxation Office provides exemplary governance frameworks that demonstrate how comprehensive oversight enables ambitious AI deployment whilst maintaining democratic accountability and public trust.
Following National Audit Office review, the ATO implemented comprehensive AI governance including formal risk management, model inventory and approval processes, bias testing protocols, and public transparency reporting. These frameworks enable extensive AI use across multiple applications whilst ensuring regulatory compliance and citizen rights protection.
The governance structure includes AI Ethics Committees with technical, legal, and external representation providing oversight of high-risk applications. Model approval processes ensure comprehensive validation including technical performance, legal compliance, and impact assessment before deployment. Ongoing monitoring tracks performance, fairness, and citizen outcomes.
Public transparency initiatives include regular parliamentary reporting on AI system use, performance outcomes, and governance activities. Published guidance documents explain approaches to AI ethics and responsible deployment, building public understanding whilst demonstrating institutional commitment to accountability.
The programme demonstrates that comprehensive governance enhances rather than constrains AI effectiveness. Clear approval processes reduce development uncertainty whilst bias testing improves system performance across different populations. Transparency builds public trust enabling more ambitious applications.
E-invoicing and CTC International Examples
Italy's Sistema di Interscambio (SdI) and Spain's Suministro Inmediato de Información (SII) demonstrate real-time transaction monitoring capabilities that transform compliance monitoring from retrospective audit to proactive oversight.
Both systems process billions of invoices annually whilst applying sophisticated analytics to detect VAT carousel fraud, missing trader schemes, and other complex evasion patterns. Real-time processing enables immediate intervention whilst suspicious patterns are fresh enough for effective investigation.
Mexico's CFDI digitalisation has broadened the tax base by approximately 150% since 2010, bringing 4.2 million micro-enterprises into formality. CFDI 4.0 continues this evolution with enhanced data quality requirements and improved analytical integration, demonstrating how digital transformation supports both compliance and economic development.
Brazil's long-running NF-e programme provides insights into sustained digital transformation over nearly two decades. Real-time validations through SEFAZ systems demonstrate how structured data standards enable both immediate business benefits and comprehensive analytical capabilities for tax authorities.
These international experiences demonstrate that successful AI deployment requires sustained commitment, comprehensive planning, robust governance, and systematic performance measurement whilst building stakeholder trust through transparency and accountability.
Italy and Spain: VAT Gap Reduction Through Real-Time Monitoring
Italy's Sistema di Interscambio (SdI) and Spain's Suministro Inmediato de Información (SII) demonstrate the transformative potential of mandatory e-invoicing systems combined with real-time analytical capabilities.
Both systems process billions of invoices annually, applying sophisticated algorithms to detect VAT carousel fraud, missing trader fraud, and other complex evasion schemes. Real-time processing enables immediate identification of suspicious patterns whilst transactions are still recent enough for effective intervention.
The EU's VAT gap data provides objective evidence of these systems' effectiveness. Countries implementing comprehensive real-time reporting show consistently lower VAT gaps compared to those relying on traditional periodic reporting. The EU-wide VAT gap averaged 7.0% in 2022, but leading CTC implementations achieve gaps below 5%.
Technical architecture employs stream processing systems that analyse transaction patterns in near real-time whilst maintaining performance standards necessary for business operations. Machine learning models identify anomalous patterns using unsupervised learning techniques, graph analysis, and time-series analysis optimised for high-velocity data streams.
Mexico: Digital Transformation and Formalisation
Mexico's CFDI (Comprobante Fiscal Digital por Internet) system demonstrates how digital transformation can simultaneously improve compliance and support economic development through business formalisation.
Since 2010, digitisation has broadened the tax base by approximately 150% whilst bringing over 4.2 million micro-enterprises into formal economic activity. CFDI 4.0 represents continued evolution with enhanced data quality requirements, strengthened identity verification, and improved integration with analytical systems.
The system's success stems from careful balance between compliance enforcement and business support. Digital invoicing reduces administrative burden for compliant businesses whilst providing tax authorities with comprehensive transaction visibility. Automated validation provides immediate feedback to businesses, reducing errors and improving compliance culture.
Brazil: Long-term Digital Infrastructure Development
Brazil's Nota Fiscal Eletrônica (NF-e) programme, operating since 2006, provides insights into long-term digital transformation sustainability and continuous improvement processes.
The programme demonstrates how sustained investment in digital infrastructure creates compound benefits over time. Real-time validation capabilities improve business process efficiency whilst providing tax authorities with unprecedented analytical capabilities. Continuous system evolution incorporates new requirements and technological advances whilst maintaining backward compatibility.
Success factors include comprehensive stakeholder engagement, phased implementation that manages change effectively, and continuous system improvement based on user feedback and operational experience. The programme's longevity demonstrates the importance of building systems for long-term evolution rather than static deployment.
These international examples provide concrete evidence that AI-enhanced tax administration can deliver substantial improvements in compliance, efficiency, and citizen service whilst maintaining democratic accountability and procedural fairness. Success patterns emphasise the importance of comprehensive planning, robust governance frameworks, systematic performance measurement, and sustained investment in both technology and human capital development.
Share this
Dinis Guarda
Author
Dinis Guarda is an author, entrepreneur, founder CEO of ztudium, Businessabc, citiesabc.com and Wisdomia.ai. Dinis is an AI leader, researcher and creator who has been building proprietary solutions based on technologies like digital twins, 3D, spatial computing, AR/VR/MR. Dinis is also an author of multiple books, including "4IR AI Blockchain Fintech IoT Reinventing a Nation" and others. Dinis has been collaborating with the likes of UN / UNITAR, UNESCO, European Space Agency, IBM, Siemens, Mastercard, and governments like USAID, and Malaysia Government to mention a few. He has been a guest lecturer at business schools such as Copenhagen Business School. Dinis is ranked as one of the most influential people and thought leaders in Thinkers360 / Rise Global’s The Artificial Intelligence Power 100, Top 10 Thought leaders in AI, smart cities, metaverse, blockchain, fintech.
previous
Ransomware Expands to VMware ESXi: Hypervisors Become a New High-Impact Target
next
The Role of Specialist Mortgage Brokers in a Complex Housing Landscape