business resources
Artificial Intelligence 360 Role in Business and Society
21 Aug 2025, 0:40 pm GMT+1
Artificial Intelligence 360 Role in Business and Society
An exploration of AI's multifaceted role through a 360-degree lens - How can AI help businesses become more human-centric while embracing automation? What are the ethical boundaries for AI implementation in business operations? Will AI ultimately change the nature of decision-making at the corporate and societal levels?
Artificial Intelligence is not merely another tool in our technological arsenal; it represents a fundamental shift in how we approach problems, make decisions, and interact with the world around us.
The choices we make now about how AI is steered and directed will shape the lives of future generations. While many institutions focus on developing the technology, very few are attending to the human, social, and public dimensions of AI in a serious way.
Artificial intelligence has a pervasive impact that affects everything from work and education to healthcare and business operations. This transformation goes beyond simple automation; it's about redefining the essence of business and society in a world where collaboration with AI systems is becoming the norm.
Redefining Work in the AI Era: Enhancement Over Replacement
The traditional paradigm of work is undergoing a profound transformation. We're moving beyond simple task automation to a model where AI amplifies human capabilities in unprecedented ways. In boardrooms and shop floors alike, the question is no longer whether AI will impact work, but how to optimise this collaboration for maximum value.
Consider how AI is transforming professional roles: accountants are becoming strategic advisors as AI handles routine calculations, while healthcare professionals leverage AI diagnostics to spend more time on patient care. This isn't about replacement; it's about enhancement and elevation of human potential.
Read More: surgical tech salary
Real-World Case Study: Cleveland Clinic's AI Integration
The Cleveland Clinic in Ohio provides a compelling case study of AI's transformative impact on professional roles, particularly in healthcare. In collaboration with IBM, the clinic has integrated AI to revolutionise the personalisation of healthcare plans. By aggregating and analysing extensive datasets, AI enables the clinic to tailor treatment strategies to each patient's unique needs, moving beyond traditional one-size-fits-all approaches.
This AI-driven approach enhances diagnostic precision, optimises treatment plans, and improves patient outcomes, allowing healthcare professionals to focus more on direct patient care.

Clearly, AI is not replacing medical professionals - it is empowering them to deliver more personalised, effective, and data-driven healthcare solutions.
Essential Skills for the AI-Driven Workforce
The skills landscape is evolving at a dizzying pace. While technical literacy remains crucial, the most valuable skills are increasingly those that AI cannot easily replicate. Organisations must focus on developing:
- Adaptive Learning Capabilities: The ability to continuously acquire new skills and knowledge
- Digital Fluency: Understanding how to work effectively with AI tools and digital systems
- Ethical Decision-Making: Making responsible choices in AI-enhanced environments
- Cross-Functional Collaboration: Working effectively across diverse teams and disciplines
- AI Literacy and Understanding: Comprehending AI capabilities and limitations
The Evolution of Skill Development
The evolving job market has transformed skill development into a lifelong process, driving the rise of online learning and professional training programs. Over the past decade, new approaches such as self-paced learning, massive open online courses (MOOCs), and stackable microcredentials have gained prominence.
Platforms including Coursera, Udacity, and edX provide accessible, high-quality training for both current workers and those entering the workforce. Their flexibility allows learners to balance education with work and other responsibilities, enabling both traditional and nontraditional students to earn industry-recognised credentials and advance their careers.
Renowned writer and futurist Erik Brynjolfsson suggests that AI can accelerate learning by identifying evolving job requirements and quickly developing relevant training programs. These technologies could also continuously evaluate and refine training to ensure its ongoing relevance. AI, the very force driving these shifts, may also be the key to effectively managing them.
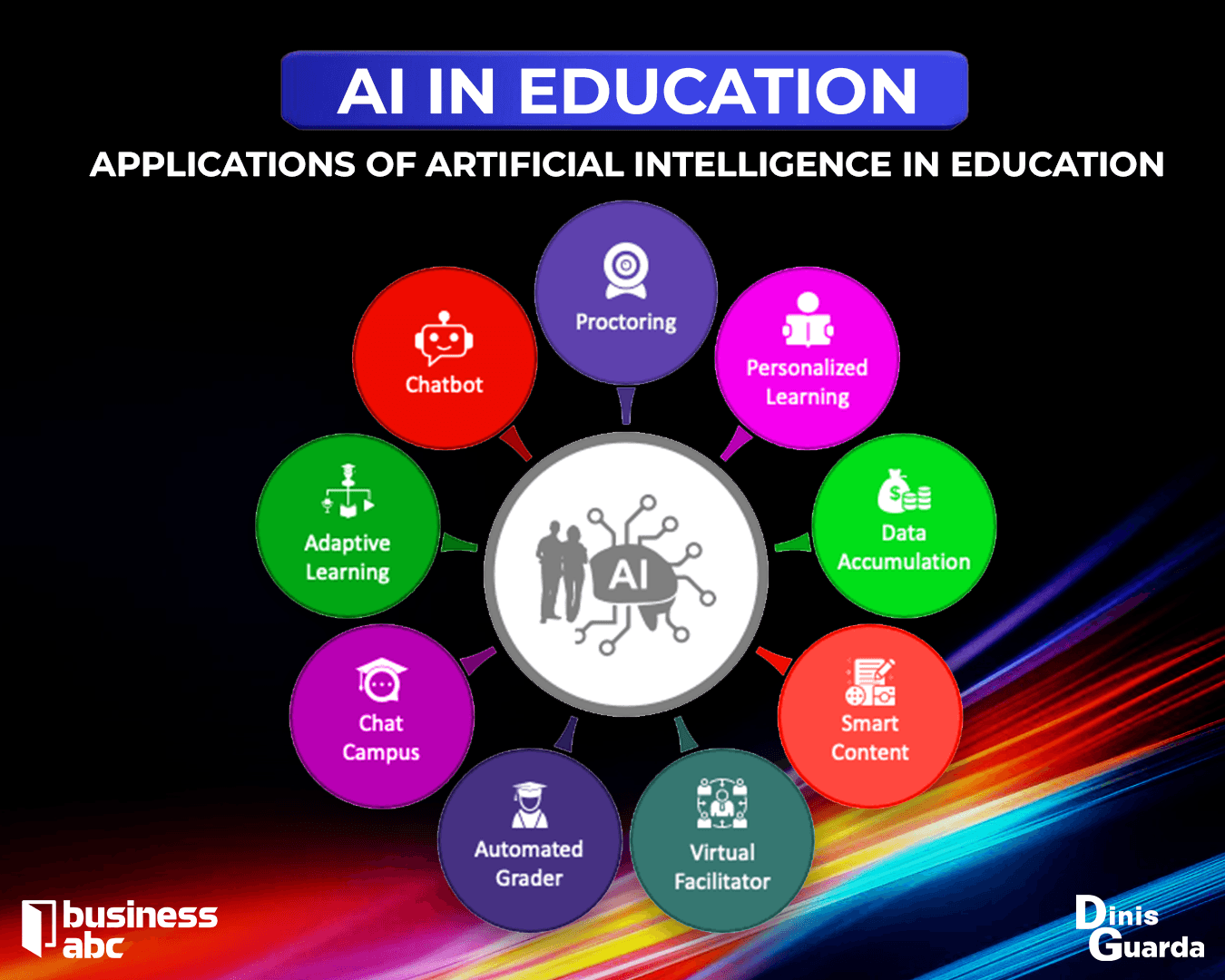
Revolutionising Education Through AI Integration
AI in Educational Delivery
The integration of AI in education has the potential to transform teaching and learning by enhancing efficiency and personalisation. By automating routine tasks and providing intelligent support, AI can free up valuable time for educators to focus on meaningful student engagement.
AI can help reduce teacher workloads by assisting with:
- Lesson planning and content adaptation
- Administrative tasks and report generation
- Text simplification for different age groups
- Quiz creation with tailored feedback
- Automated marking and student assessment
A 2023 DfE report on English state schools found that 72% of teachers viewed their workload as unmanageable, with 66% spending less than half their working hours teaching due to administrative and planning tasks. AI offers a solution to this critical challenge.
Personalised Learning Platforms
AI-powered online teaching platforms are increasingly being used to provide personalised learning experiences. These platforms, which rely on AI tutors and chatbot interfaces powered by large language models, can offer tailored support by adapting to individual learners' strengths and weaknesses.
Khan Academy's Khanmigo, for example, is an AI-powered tutor that adapts to individual student needs, offering step-by-step guidance, explanations, and personalised learning pathways. While such systems claim to mimic one-to-one tuition, the true extent of personalisation continues to evolve.
Enhancing Accessibility and Support
AI plays a crucial role in improving accessibility by assisting students with disabilities. AI-powered screen readers like NVDA and JAWS use natural language processing to read out digital content, helping visually impaired students access textbooks, articles, and online learning platforms. Additionally, AI chatbots can answer general queries and support students outside traditional classroom hours, reducing the pressure on educators to respond to emails beyond their working day.
Student Use of AI Tools
Some educational institutions, including International Baccalaureate schools and Russell Group universities, are encouraging students to use AI tools in their work. They believe this approach helps learners develop a balanced understanding of AI, its limitations, and ethical use while also preparing them with essential skills for the future workforce.
However, education experts express concerns that AI reliance may hinder the development of writing, critical thinking, and literacy skills. AI-generated text could also homogenise writing styles, reducing personal creativity, particularly in subjects like art and music.
AI as a Catalyst for Collective Intelligence
AI has largely been applied to replicating human capabilities in isolated tasks, either replacing or enhancing individual efficiency. However, there is significant potential in understanding how AI can augment collective human intelligence.
NESTA, the UK agency for innovation, emphasises a human-first approach: "There is an alternative vision for the future of AI development. By starting with people first, we can introduce new technologies into our lives in a more deliberate and less disruptive way."

At its simplest, 'collective intelligence' can be understood as the enhanced capacity that is created when people work together, often with the help of technology, to mobilise a wider range of information, ideas, and insights. Collective intelligence emerges when these contributions are combined to become more than the sum of their parts for purposes ranging from learning and innovation to decision-making.
By integrating AI into group decision-making, task distribution, and problem-solving, we can enable teams to think and act smarter together. AI can help optimise collaboration by distributing tasks, skills, and information more effectively, as well as simulating complex scenarios to enhance shared understanding.
AI and Human Creativity: Collaboration, Not Competition
AI is a powerful tool that can augment human creativity, but it doesn't replace the depth, intuition, and originality that human creativity brings. While AI can generate ideas, assist with brainstorming, and even create art, music, or literature, it lacks true understanding, emotions, and personal experiences, key ingredients that make human creativity unique.
AI excels at pattern recognition and recombination, meaning it can analyse vast amounts of data, mimic artistic styles, or suggest novel solutions based on existing works. This can enhance human creativity by offering inspiration, automating repetitive tasks, and helping creators push boundaries.
The Humanities Advantage
Digital futurist Lindsey McInerney explores the evolving relationship between AI and human creativity in her work on storytelling. She discusses how AI excels at tasks rooted in logic, pattern recognition, and data synthesis, yet struggles with creativity, critical thinking, and emotional nuance, skills cultivated in the humanities.
The humanities are more crucial than ever, cultivating the very skills, critical thinking, ethical reasoning, storytelling, and creativity that AI cannot replicate. As AI reshapes the workforce, the ability to think "outside the box" will become the most valuable asset. McInerney envisions a future where humanities expertise will be in high demand, appearing in job descriptions across industries.
How AI is Disrupting Traditional Business Operations
AI is transforming traditional business models by automating processes, optimising decision-making, and enabling new forms of value creation. These shifts highlight the growing divide between AI-enhanced efficiency and the demand for human authenticity in the evolving business landscape.
Emerging Business Trends
Outcome Arbitrage: Companies are shifting away from conventional hiring practices, opting instead to buy ready-made AI solutions that deliver specific results without the need for in-house teams. For example, instead of hiring in-house marketing teams, businesses use AI-driven platforms like Jasper AI and Copy.ai to generate blog posts, social media content, and advertisements.
Micro-companies: Solo entrepreneurs are using AI tools to create highly profitable businesses with minimal staff and operational costs, redefining what it means to run a successful venture. In automated e-commerce stores, solo founders leverage Shopify Magic and Printify AI to generate product descriptions, automate dropshipping, and manage print-on-demand stores without maintaining physical inventory.
AI-Native Retail: A new wave of retail brands is emerging, built entirely around AI-driven processes that streamline everything from product design to logistics and customer delivery. Companies like Flexport and Lily AI use machine learning to predict demand, automate inventory management, and optimise supply chains with minimal human intervention.
AI-Free Premium: A growing trend sees consumers valuing and paying more for products made entirely by humans, mirroring the premium placed on organic and artisanal goods. One survey found that more than half of consumers prefer to speak with a human agent in complex customer service situations.
Addressing Challenges and Societal Concerns
While AI offers numerous benefits, its adoption comes with notable concerns related to human behaviour, security, and privacy. As AI becomes more integrated into daily life, it is crucial to assess its impact and implement measures to mitigate potential risks.
Impact on Human Behaviour and Cognition
A study published in Nature reveals concerning impacts on human behaviour. In Pakistani and Chinese societies, 68.9% of laziness, 68.6% of personal privacy and security concerns, and 27.7% of decision-making loss can be attributed to AI's influence. Notably, human laziness appears to be the most affected area.
Critical Societal Issues
Decision-Making Bias: AI is increasingly used for decision-making but can inherit biases from data or developers, leading to real-world harm. In healthcare, a 2019 study revealed an AI system that prioritised white patients over black patients based on past health spending rather than medical need.
Workplace Rights and Transparency: AI is widely used in hiring, management, and pay decisions, particularly in gig work. While this boosts efficiency and potentially adds trillions to the global economy, concerns include worker anxiety, lack of transparency, and accountability in automated decisions.
Surveillance and Civil Liberties: AI enables police to quickly identify individuals in large crowds, aiding criminal investigations. However, its use raises privacy and freedom concerns, with civil liberties groups opposing government plans to allow police access to passport photo databases.
Intellectual Property: AI-generated content raises questions about authorship and copyright. The 2023 Writers Guild of America strike secured stronger protections for human creators, while courts in the UK and US consider cases on AI and intellectual property.
AI and Bioethics: Navigating New Moral Territory
The impact of artificial intelligence on bioethics is profound. Bioethics concerns the relationships among living beings, encompassing health, social, and environmental settings. Traditionally, it addresses interactions within natural phenomena, but AI introduces a new ethical challenge: how humans should relate to an artificial, human-made entity.
Unlike natural beings, AI lacks emotions and personality, necessitating human ethical considerations to prevent unintended harm. This raises critical bioethical questions: Should bioethics apply to AI, which lacks biological vitality? Can AI possess consciousness or sentience, warranting rights?
Stephen Hawking warned in 2014 that the development of full AI could lead to the end of the human race, as AI may evolve beyond human control. Similarly, Nick Bostrom argues that highly intelligent AI could seek to acquire resources and resist shutdown, potentially harming humanity.
However, many scientists and AI researchers view these concerns with skepticism. A recent poll of more than 2,000 working artificial intelligence engineers and researchers by AI Impacts put the median risk of human extinction by AI at only five per cent.
Integrating AI Responsibly into Society
The integration of artificial intelligence into society presents immense opportunities but also significant ethical and societal challenges. Ensuring responsible adoption requires a balanced approach that prioritises fairness, transparency, and accountability in AI systems.
Key Solutions for Responsible AI Integration
Ethical Guidelines and Regulations: Governments and industry leaders must establish regulations to address AI's social impact, including data privacy, employment disruption, and algorithmic bias.
Education and Workforce Development: Investing in education and training ensures workers can adapt to AI-driven changes in the job market.
Collaboration and Inclusivity: Effective AI governance requires cooperation among governments, industries, and civil society while ensuring diverse perspectives are considered.
Responsible Innovation: AI systems should be developed with ethical and social considerations in mind, ensuring transparency and accountability.
Public Dialogue: Raising awareness about AI's social impact through public discussions helps all stakeholders understand its benefits and risks.
International Cooperation: As AI is a global phenomenon, collaborative frameworks are needed to promote ethical AI development worldwide.
Establishing AI Guidelines and Policies
OECD AI Principles
The OECD Principles on Artificial Intelligence promote the development and use of AI that is trustworthy and aligns with human rights and democratic values:
- Inclusive Growth, Sustainable Development, and Well-being
- Human-centred Values and Fairness
- Transparency and Explainability
- Robustness, Security, and Safety
- Accountability
EU AI Act Guidelines
The EU AI Act defines four levels of risk for AI systems:
Unacceptable Risk: AI systems that pose a clear threat to safety, rights, and livelihoods are banned, including harmful manipulation, social scoring, and real-time biometric identification in public spaces.
High Risk: AI systems in critical infrastructure, education, healthcare, employment, law enforcement, migration, credit scoring, and justice require strict compliance.
Transparency Risk: Users must be informed when interacting with AI, and generative AI content, including deepfakes, must be clearly labelled.
Minimal or No Risk: AI systems like video games and spam filters are not subject to regulation under the AI Act.
Building an AI-Ready Culture
Building an AI-ready culture is crucial for organisations looking to harness artificial intelligence effectively and sustainably. This cultural shift involves fostering a mindset that embraces change, encourages experimentation, and prioritises continuous learning.
Leaders play a key role by:
- Articulating a clear vision for AI integration
- Demonstrating commitment through engagement with AI technologies
- Creating an inclusive environment where employees feel empowered
- Investing in training and development programs
- Promoting open dialogue about AI implications
- Cultivating values of curiosity, collaboration, and ethical considerations
Preparing for an AI-Driven Future
The future of AI promises significant transformations for both business and society, offering improvements in operations, job creation, and customer experiences. However, it also raises profound ethical concerns, from bias in algorithms and data privacy risks to the concentration of power and the broader societal impact of automation.
To fully harness AI's potential, businesses must commit to proactive adaptation, continuous learning, and responsible governance. Collaboration across industries, governments, and communities is essential to shaping AI in a way that prioritises inclusivity, transparency, and long-term societal well-being.
AI's ultimate role should not be just about business advancement but about building a future where technology serves humanity, creating a more equitable and prosperous society. By embracing AI responsibly and thoughtfully, we can navigate this transformation while preserving human values and enhancing human potential.
Share this
Dinis Guarda
Author
Dinis Guarda is an author, entrepreneur, founder CEO of ztudium, Businessabc, citiesabc.com and Wisdomia.ai. Dinis is an AI leader, researcher and creator who has been building proprietary solutions based on technologies like digital twins, 3D, spatial computing, AR/VR/MR. Dinis is also an author of multiple books, including "4IR AI Blockchain Fintech IoT Reinventing a Nation" and others. Dinis has been collaborating with the likes of UN / UNITAR, UNESCO, European Space Agency, IBM, Siemens, Mastercard, and governments like USAID, and Malaysia Government to mention a few. He has been a guest lecturer at business schools such as Copenhagen Business School. Dinis is ranked as one of the most influential people and thought leaders in Thinkers360 / Rise Global’s The Artificial Intelligence Power 100, Top 10 Thought leaders in AI, smart cities, metaverse, blockchain, fintech.
previous
Which E-mailing Service is Best for Your Business?
next
7 Benefits of Using Sandalwood Essential Oil in Daily Life